Infection
Understanding virus–host interactions in tissues
Abstract
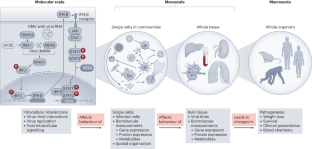
Although virus–host interactions are usually studied in a single cell type using in vitro assays in immortalized cell lines or isolated cell populations, it is important to remember that what is happening inside one infected cell does not translate to understanding how an infected cell behaves in a tissue, organ or whole organism. Infections occur in complex tissue environments, which contain a host of factors that can alter the course of the infection, including immune cells, non-immune cells and extracellular-matrix components. These factors affect how the host responds to the virus and form the basis of the protective response. To understand virus infection, tools are needed that can profile the tissue environment. This Review highlights methods to study virus–host interactions in the infection microenvironment.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
style{display:none!important}.LiveAreaSection-193358632 *{align-content:stretch;align-items:stretch;align-self:auto;animation-delay:0s;animation-direction:normal;animation-duration:0s;animation-fill-mode:none;animation-iteration-count:1;animation-name:none;animation-play-state:running;animation-timing-function:ease;azimuth:center;backface-visibility:visible;background-attachment:scroll;background-blend-mode:normal;background-clip:borderBox;background-color:transparent;background-image:none;background-origin:paddingBox;background-position:0 0;background-repeat:repeat;background-size:auto auto;block-size:auto;border-block-end-color:currentcolor;border-block-end-style:none;border-block-end-width:medium;border-block-start-color:currentcolor;border-block-start-style:none;border-block-start-width:medium;border-bottom-color:currentcolor;border-bottom-left-radius:0;border-bottom-right-radius:0;border-bottom-style:none;border-bottom-width:medium;border-collapse:separate;border-image-outset:0s;border-image-repeat:stretch;border-image-slice:100%;border-image-source:none;border-image-width:1;border-inline-end-color:currentcolor;border-inline-end-style:none;border-inline-end-width:medium;border-inline-start-color:currentcolor;border-inline-start-style:none;border-inline-start-width:medium;border-left-color:currentcolor;border-left-style:none;border-left-width:medium;border-right-color:currentcolor;border-right-style:none;border-right-width:medium;border-spacing:0;border-top-color:currentcolor;border-top-left-radius:0;border-top-right-radius:0;border-top-style:none;border-top-width:medium;bottom:auto;box-decoration-break:slice;box-shadow:none;box-sizing:border-box;break-after:auto;break-before:auto;break-inside:auto;caption-side:top;caret-color:auto;clear:none;clip:auto;clip-path:none;color:initial;column-count:auto;column-fill:balance;column-gap:normal;column-rule-color:currentcolor;column-rule-style:none;column-rule-width:medium;column-span:none;column-width:auto;content:normal;counter-increment:none;counter-reset:none;cursor:auto;display:inline;empty-cells:show;filter:none;flex-basis:auto;flex-direction:row;flex-grow:0;flex-shrink:1;flex-wrap:nowrap;float:none;font-family:initial;font-feature-settings:normal;font-kerning:auto;font-language-override:normal;font-size:medium;font-size-adjust:none;font-stretch:normal;font-style:normal;font-synthesis:weight style;font-variant:normal;font-variant-alternates:normal;font-variant-caps:normal;font-variant-east-asian:normal;font-variant-ligatures:normal;font-variant-numeric:normal;font-variant-position:normal;font-weight:400;grid-auto-columns:auto;grid-auto-flow:row;grid-auto-rows:auto;grid-column-end:auto;grid-column-gap:0;grid-column-start:auto;grid-row-end:auto;grid-row-gap:0;grid-row-start:auto;grid-template-areas:none;grid-template-columns:none;grid-template-rows:none;height:auto;hyphens:manual;image-orientation:0deg;image-rendering:auto;image-resolution:1dppx;ime-mode:auto;inline-size:auto;isolation:auto;justify-content:flexStart;left:auto;letter-spacing:normal;line-break:auto;line-height:normal;list-style-image:none;list-style-position:outside;list-style-type:disc;margin-block-end:0;margin-block-start:0;margin-bottom:0;margin-inline-end:0;margin-inline-start:0;margin-left:0;margin-right:0;margin-top:0;mask-clip:borderBox;mask-composite:add;mask-image:none;mask-mode:matchSource;mask-origin:borderBox;mask-position:0 0;mask-repeat:repeat;mask-size:auto;mask-type:luminance;max-height:none;max-width:none;min-block-size:0;min-height:0;min-inline-size:0;min-width:0;mix-blend-mode:normal;object-fit:fill;object-position:50% 50%;offset-block-end:auto;offset-block-start:auto;offset-inline-end:auto;offset-inline-start:auto;opacity:1;order:0;orphans:2;outline-color:initial;outline-offset:0;outline-style:none;outline-width:medium;overflow:visible;overflow-wrap:normal;overflow-x:visible;overflow-y:visible;padding-block-end:0;padding-block-start:0;padding-bottom:0;padding-inline-end:0;padding-inline-start:0;padding-left:0;padding-right:0;padding-top:0;page-break-after:auto;page-break-before:auto;page-break-inside:auto;perspective:none;perspective-origin:50% 50%;pointer-events:auto;position:static;quotes:initial;resize:none;right:auto;ruby-align:spaceAround;ruby-merge:separate;ruby-position:over;scroll-behavior:auto;scroll-snap-coordinate:none;scroll-snap-destination:0 0;scroll-snap-points-x:none;scroll-snap-points-y:none;scroll-snap-type:none;shape-image-threshold:0;shape-margin:0;shape-outside:none;tab-size:8;table-layout:auto;text-align:initial;text-align-last:auto;text-combine-upright:none;text-decoration-color:currentcolor;text-decoration-line:none;text-decoration-style:solid;text-emphasis-color:currentcolor;text-emphasis-position:over right;text-emphasis-style:none;text-indent:0;text-justify:auto;text-orientation:mixed;text-overflow:clip;text-rendering:auto;text-shadow:none;text-transform:none;text-underline-position:auto;top:auto;touch-action:auto;transform:none;transform-box:borderBox;transform-origin:50% 50%0;transform-style:flat;transition-delay:0s;transition-duration:0s;transition-property:all;transition-timing-function:ease;vertical-align:baseline;visibility:visible;white-space:normal;widows:2;width:auto;will-change:auto;word-break:normal;word-spacing:normal;word-wrap:normal;writing-mode:horizontalTb;z-index:auto;-webkit-appearance:none;-moz-appearance:none;-ms-appearance:none;appearance:none;margin:0}.LiveAreaSection-193358632{width:100%}.LiveAreaSection-193358632 .login-option-buybox{display:block;width:100%;font-size:17px;line-height:30px;color:#222;padding-top:30px;font-family:Harding,Palatino,serif}.LiveAreaSection-193358632 .additional-access-options{display:block;font-weight:700;font-size:17px;line-height:30px;color:#222;font-family:Harding,Palatino,serif}.LiveAreaSection-193358632 .additional-login>li:not(:first-child)::before{transform:translateY(-50%);content:””;height:1rem;position:absolute;top:50%;left:0;border-left:2px solid #999}.LiveAreaSection-193358632 .additional-login>li:not(:first-child){padding-left:10px}.LiveAreaSection-193358632 .additional-login>li{display:inline-block;position:relative;vertical-align:middle;padding-right:10px}.BuyBoxSection-683559780{display:flex;flex-wrap:wrap;flex:1;flex-direction:row-reverse;margin:-30px -15px 0}.BuyBoxSection-683559780 .box-inner{width:100%;height:100%}.BuyBoxSection-683559780 .readcube-buybox{background-color:#f3f3f3;flex-shrink:1;flex-grow:1;flex-basis:255px;background-clip:content-box;padding:0 15px;margin-top:30px}.BuyBoxSection-683559780 .subscribe-buybox{background-color:#f3f3f3;flex-shrink:1;flex-grow:4;flex-basis:300px;background-clip:content-box;padding:0 15px;margin-top:30px}.BuyBoxSection-683559780 .subscribe-buybox-nature-plus{background-color:#f3f3f3;flex-shrink:1;flex-grow:4;flex-basis:100%;background-clip:content-box;padding:0 15px;margin-top:30px}.BuyBoxSection-683559780 .title-readcube,.BuyBoxSection-683559780 .title-buybox{display:block;margin:0;margin-right:10%;margin-left:10%;font-size:24px;line-height:32px;color:#222;padding-top:30px;text-align:center;font-family:Harding,Palatino,serif}.BuyBoxSection-683559780 .title-asia-buybox{display:block;margin:0;margin-right:5%;margin-left:5%;font-size:24px;line-height:32px;color:#222;padding-top:30px;text-align:center;font-family:Harding,Palatino,serif}.BuyBoxSection-683559780 .asia-link{color:#069;cursor:pointer;text-decoration:none;font-size:1.05em;font-family:-apple-system,BlinkMacSystemFont,”Segoe UI”,Roboto,Oxygen-Sans,Ubuntu,Cantarell,”Helvetica Neue”,sans-serif;line-height:1.05em6}.BuyBoxSection-683559780 .access-readcube{display:block;margin:0;margin-right:10%;margin-left:10%;font-size:14px;color:#222;padding-top:10px;text-align:center;font-family:-apple-system,BlinkMacSystemFont,”Segoe UI”,Roboto,Oxygen-Sans,Ubuntu,Cantarell,”Helvetica Neue”,sans-serif;line-height:20px}.BuyBoxSection-683559780 .access-asia-buybox{display:block;margin:0;margin-right:5%;margin-left:5%;font-size:14px;color:#222;padding-top:10px;text-align:center;font-family:-apple-system,BlinkMacSystemFont,”Segoe UI”,Roboto,Oxygen-Sans,Ubuntu,Cantarell,”Helvetica Neue”,sans-serif;line-height:20px}.BuyBoxSection-683559780 .access-buybox{display:block;margin:0;margin-right:10%;margin-left:10%;font-size:14px;color:#222;opacity:.8px;padding-top:10px;text-align:center;font-family:-apple-system,BlinkMacSystemFont,”Segoe UI”,Roboto,Oxygen-Sans,Ubuntu,Cantarell,”Helvetica Neue”,sans-serif;line-height:20px}.BuyBoxSection-683559780 .price-buybox{display:block;font-size:30px;color:#222;font-family:-apple-system,BlinkMacSystemFont,”Segoe UI”,Roboto,Oxygen-Sans,Ubuntu,Cantarell,”Helvetica Neue”,sans-serif;padding-top:30px;text-align:center}.BuyBoxSection-683559780 .price-buybox-to{display:block;font-size:30px;color:#222;font-family:-apple-system,BlinkMacSystemFont,”Segoe UI”,Roboto,Oxygen-Sans,Ubuntu,Cantarell,”Helvetica Neue”,sans-serif;text-align:center}.BuyBoxSection-683559780 .price-info-text{font-size:16px;padding-right:10px;color:#222;font-family:-apple-system,BlinkMacSystemFont,”Segoe UI”,Roboto,Oxygen-Sans,Ubuntu,Cantarell,”Helvetica Neue”,sans-serif}.BuyBoxSection-683559780 .price-value{font-size:30px;font-family:-apple-system,BlinkMacSystemFont,”Segoe UI”,Roboto,Oxygen-Sans,Ubuntu,Cantarell,”Helvetica Neue”,sans-serif}.BuyBoxSection-683559780 .price-per-period{font-family:-apple-system,BlinkMacSystemFont,”Segoe UI”,Roboto,Oxygen-Sans,Ubuntu,Cantarell,”Helvetica Neue”,sans-serif}.BuyBoxSection-683559780 .price-from{font-size:14px;padding-right:10px;color:#222;font-family:-apple-system,BlinkMacSystemFont,”Segoe UI”,Roboto,Oxygen-Sans,Ubuntu,Cantarell,”Helvetica Neue”,sans-serif;line-height:20px}.BuyBoxSection-683559780 .issue-buybox{display:block;font-size:13px;text-align:center;color:#222;font-family:-apple-system,BlinkMacSystemFont,”Segoe UI”,Roboto,Oxygen-Sans,Ubuntu,Cantarell,”Helvetica Neue”,sans-serif;line-height:19px}.BuyBoxSection-683559780 .no-price-buybox{display:block;font-size:13px;line-height:18px;text-align:center;padding-right:10%;padding-left:10%;padding-bottom:20px;padding-top:30px;color:#222;font-family:-apple-system,BlinkMacSystemFont,”Segoe UI”,Roboto,Oxygen-Sans,Ubuntu,Cantarell,”Helvetica Neue”,sans-serif}.BuyBoxSection-683559780 .vat-buybox{display:block;margin-top:5px;margin-right:20%;margin-left:20%;font-size:11px;color:#222;padding-top:10px;padding-bottom:15px;text-align:center;font-family:-apple-system,BlinkMacSystemFont,”Segoe UI”,Roboto,Oxygen-Sans,Ubuntu,Cantarell,”Helvetica Neue”,sans-serif;line-height:17px}.BuyBoxSection-683559780 .tax-buybox{display:block;width:100%;color:#222;padding:20px 16px;text-align:center;font-family:-apple-system,BlinkMacSystemFont,”Segoe UI”,Roboto,Oxygen-Sans,Ubuntu,Cantarell,”Helvetica Neue”,sans-serif;line-height:NaNpx}.BuyBoxSection-683559780 .button-container{display:flex;padding-right:20px;padding-left:20px;justify-content:center}.BuyBoxSection-683559780 .button-container>*{flex:1px}.BuyBoxSection-683559780 .button-container>a:hover,.Button-505204839:hover,.Button-1078489254:hover,.Button-2496381730:hover{text-decoration:none}.BuyBoxSection-683559780 .readcube-button{background:#fff;margin-top:30px}.BuyBoxSection-683559780 .button-asia{background:#069;border:1px solid #069;border-radius:0;cursor:pointer;display:block;padding:9px;outline:0;text-align:center;text-decoration:none;min-width:80px;margin-top:75px}.BuyBoxSection-683559780 .button-label-asia,.ButtonLabel-3869432492,.ButtonLabel-3296148077,.ButtonLabel-1651148777{display:block;color:#fff;font-size:17px;line-height:20px;font-family:-apple-system,BlinkMacSystemFont,”Segoe UI”,Roboto,Oxygen-Sans,Ubuntu,Cantarell,”Helvetica Neue”,sans-serif;text-align:center;text-decoration:none;cursor:pointer}.Button-505204839,.Button-1078489254,.Button-2496381730{background:#069;border:1px solid #069;border-radius:0;cursor:pointer;display:block;padding:9px;outline:0;text-align:center;text-decoration:none;min-width:80px;max-width:320px;margin-top:10px}.Button-505204839 .readcube-label,.Button-1078489254 .readcube-label,.Button-2496381730 .readcube-label{color:#069}
/* style specs end */
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$29.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Rent or buy this article
Prices vary by article type
from$1.95
to$39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


References
-
Anderson, N. M. & Simon, M. C. The tumor microenvironment. Curr. Biol. 30, R921–R925 (2020).
Google Scholar
-
Roma-Rodrigues, C., Mendes, R., Baptista, P. V. & Fernandes, A. R. Targeting tumor microenvironment for cancer therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 20, 840 (2019).
Google Scholar
-
Reid, S. P. et al. Ebola virus VP24 binds karyopherin α1 and blocks STAT1 nuclear accumulation. J. Virol. 80, 5156–5167 (2006).
Google Scholar
-
Woolsey, C. et al. A VP35 mutant Ebola virus lacks virulence but can elicit protective immunity to wild-type virus challenge. Cell Rep. 28, 3032–3046 (2019).
Google Scholar
-
Caballero, I. S. et al. In vivo Ebola virus infection leads to a strong innate response in circulating immune cells. BMC Genomics 17, 707 (2016).
Google Scholar
-
Liu, X. et al. Transcriptomic signatures differentiate survival from fatal outcomes in humans infected with Ebola virus. Genome Biol. 18, 4 (2017).
Google Scholar
-
Speranza, E. et al. Previremic identification of Ebola or Marburg virus infection using integrated host-transcriptome and viral genome detection. mBio 11, e01157-20 (2020).
Google Scholar
-
Wong, H. S. & Germain, R. N. Mesoscale T cell antigen discrimination emerges from intercellular feedback. Trends Immunol. 42, 865–875 (2021).
Google Scholar
-
Germain, R. N. et al. Understanding immunity in a tissue-centric context: combining novel imaging methods and mathematics to extract new insights into function and dysfunction. Immunol. Rev. 306, 8–24 (2022).
Google Scholar
-
Gola, A. et al. Commensal-driven immune zonation of the liver promotes host defence. Nature 589, 131–136 (2021).
Google Scholar
-
Bjarnsholt, T. et al. The importance of understanding the infectious microenvironment. Lancet Infect. Dis. 22, e88–e92 (2022).
Google Scholar
-
Depledge, D. P., Mohr, I. & Wilson, A. C. Going the distance: optimizing RNA-Seq strategies for transcriptomic analysis of complex viral genomes. J. Virol. 93, e01342-18 (2019).
Google Scholar
-
Newman, A. M. et al. Determining cell type abundance and expression from bulk tissues with digital cytometry. Nat. Biotechnol. 37, 773–782 (2019).
Google Scholar
-
Sun, X., Sun, S. & Yang, S. An efficient and flexible method for deconvoluting bulk RNA-Seq data with single-cell RNA-Seq data. Cells 8, 1161 (2019).
Google Scholar
-
Newman, A. M. et al. Robust enumeration of cell subsets from tissue expression profiles. Nat. Methods 12, 453–457 (2015).
Google Scholar
-
Tsalik, E. L. et al. The host response to viral infections reveals common and virus-specific signatures in the peripheral blood. Front Immunol. 12, 741837 (2021).
Google Scholar
-
Wang, R. Y. L., Weng, K. F., Huang, Y. C. & Chen, C. J. Elevated expression of circulating miR876-5p is a specific response to severe EV71 infections. Sci. Rep. 6, 24149 (2016).
Google Scholar
-
Speranza, E. et al. T-cell receptor diversity and the control of T-cell homeostasis mark Ebola virus disease survival in humans. J. Infect. Dis. 218, S508–S518 (2018).
Google Scholar
-
Speranza, E. et al. Comparison of transcriptomic platforms for analysis of whole blood from Ebola-infected cynomolgus macaques. Sci. Rep. 7, 14756 (2017).
Google Scholar
-
Warren, S. in Gene Expression Analysis: Methods and Protocols (eds Raghavachari, N. & Garcia-Reyero, N.) 105–120 (Springer New York, 2018).
-
Quick, J. et al. Multiplex PCR method for MinION and Illumina sequencing of Zika and other virus genomes directly from clinical samples. Nat. Protoc. 12, 1261–1276 (2017).
Google Scholar
-
Wang, J., Moore, N. E., Deng, Y. M., Eccles, D. A. & Hall, R. J. MinION nanopore sequencing of an influenza genome. Front. Microbiol. 6, 766 (2015).
Google Scholar
-
Yakovleva, A. et al. Tracking SARS-COV-2 variants using nanopore sequencing in Ukraine in 2021. Sci. Rep. 12, 15749 (2022).
Google Scholar
-
Buenrostro, J. D., Wu, B., Chang, H. Y. & Greenleaf, W. J. ATAC–Seq: a method for assaying chromatin accessibility genome-wide. Curr. Protoc. Mol. Biol. 109, 21.29.21–21.29.29 (2015).
Google Scholar
-
Scott-Browne, J. P. et al. Dynamic changes in chromatin accessibility occur in CD8+ T cells responding to viral infection. Immunity 45, 1327–1340 (2016).
Google Scholar
-
Bruzzone, C. et al. SARS-CoV-2 infection dysregulates the metabolomic and lipidomic profiles of serum. iScience 23, 101645 (2020).
Google Scholar
-
Schwarz, B. et al. Cutting Edge: Severe SARS-CoV-2 infection in humans is defined by a shift in the serum lipidome, resulting in dysregulation of eicosanoid immune mediators. J. Immunol. 206, 329–334 (2021).
Google Scholar
-
Speranza, E. et al. Age-related differences in immune dynamics during SARS-CoV-2 infection in rhesus macaques. Life Sci. Alliance 5, e202101314 (2022).
Google Scholar
-
Roberts, L. M. et al. Pulmonary infection induces persistent, pathogen-specific lipidomic changes influencing trained immunity. iScience 24, 103025 (2021).
Google Scholar
-
Barberis, E. et al. Understanding protection from SARS-CoV-2 using metabolomics. Sci. Rep. 11, 13796 (2021).
Google Scholar
-
Cui, L. et al. Metabolomics investigation reveals metabolite mediators associated with acute lung injury and repair in a murine model of influenza pneumonia. Sci. Rep. 6, 26076 (2016).
Google Scholar
-
Gerner, M. Y., Kastenmuller, W., Ifrim, I., Kabat, J. & Germain, R. N. Histo-cytometry: a method for highly multiplex quantitative tissue imaging analysis applied to dendritic cell subset microanatomy in lymph nodes. Immunity 37, 364–376 (2012).
Google Scholar
-
Mathew, D. et al. Deep immune profiling of COVID-19 patients reveals distinct immunotypes with therapeutic implications. Science 369, eabc8511 (2020).
Google Scholar
-
Holmes, K. L. Characterization of aerosols produced by cell sorters and evaluation of containment. Cytometry A 79, 1000–1008 (2011).
Google Scholar
-
Robinson, J. P. Flow cytometry: past and future. Biotechniques 72, 159–169 (2022).
Google Scholar
-
Park, L. M., Lannigan, J. & Jaimes, M. C. OMIP-069: forty-color full spectrum flow cytometry panel for deep immunophenotyping of major cell subsets in human peripheral blood. Cytometry A 97, 1044–1051 (2020).
Google Scholar
-
Bendall, S. C. et al. Single-cell mass cytometry of differential immune and drug responses across a human hematopoietic continuum. Science 332, 687–696 (2011).
Google Scholar
-
Bodenmiller, B. et al. Multiplexed mass cytometry profiling of cellular states perturbed by small-molecule regulators. Nat. Biotechnol. 30, 858–867 (2012).
Google Scholar
-
Leelatian, N. et al. Unsupervised machine learning reveals risk stratifying glioblastoma tumor cells. eLife 9, e56879 (2020).
Google Scholar
-
Lee, J. S. et al. Single-cell transcriptome of bronchoalveolar lavage fluid reveals sequential change of macrophages during SARS-CoV-2 infection in ferrets. Nat. Commun. 12, 4567 (2021).
Google Scholar
-
Johnson, M. B. et al. Single-cell analysis reveals transcriptional heterogeneity of neural progenitors in human cortex. Nat. Neurosci. 18, 637–646 (2015).
Google Scholar
-
Meyer, M. et al. Attenuated activation of pulmonary immune cells in mRNA-1273-vaccinated hamsters after SARS-CoV-2 infection. J. Clin. Invest. 131, e148036 (2021).
Google Scholar
-
Nouailles, G. et al. Temporal omics analysis in Syrian hamsters unravel cellular effector responses to moderate COVID-19. Nat. Commun. 12, 4869 (2021).
Google Scholar
-
Friedrichs, V. et al. Landscape and age dynamics of immune cells in the Egyptian rousette bat. Cell Rep. 40, 111305 (2022).
Google Scholar
-
Wang, X., Yu, L. & Wu, A. R. The effect of methanol fixation on single-cell RNA sequencing data. BMC Genomics 22, 420 (2021).
Google Scholar
-
Phan, H. V. et al. High-throughput RNA sequencing of paraformaldehyde-fixed single cells. Nat. Commun. 12, 5636 (2021).
Google Scholar
-
Logue, J. et al. in Global Virology III: Virology in the 21st Century (eds Shapshak, P. et al.) 437–469 (Springer International Publishing, 2019).
-
Gierahn, T. M. et al. Seq-Well: portable, low-cost RNA sequencing of single cells at high throughput. Nat. Methods 14, 395–398 (2017).
Google Scholar
-
Clark, I. C. et al. Microfluidics-free single-cell genomics with templated emulsification. Nat. Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41587-023-01685-z (2023).
-
Tian, Y. et al. Single-cell immunology of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Nat. Biotechnol. 40, 30–41 (2022).
Google Scholar
-
Delorey, T. M. et al. COVID-19 tissue atlases reveal SARS-CoV-2 pathology and cellular targets. Nature 595, 107–113 (2021).
Google Scholar
-
Liu, C. et al. Time-resolved systems immunology reveals a late juncture linked to fatal COVID-19. Cell 184, 1836–1857 (2021).
Google Scholar
-
Loske, J. et al. Pre-activated antiviral innate immunity in the upper airways controls early SARS-CoV-2 infection in children. Nat. Biotechnol. 40, 319–324 (2022).
Google Scholar
-
Chua, R. L. et al. COVID-19 severity correlates with airway epithelium–immune cell interactions identified by single-cell analysis. Nat. Biotechnol. 38, 970–979 (2020).
Google Scholar
-
Garcia-Flores, V. et al. Maternal-fetal immune responses in pregnant women infected with SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Commun. 13, 320 (2022).
Google Scholar
-
Kotliar, D. et al. Single-cell profiling of Ebola virus disease in vivo reveals viral and host dynamics. Cell 183, 1383–1401 (2020).
Google Scholar
-
Zanini, F., Pu, S. Y., Bekerman, E., Einav, S. & Quake, S. R. Single-cell transcriptional dynamics of flavivirus infection. eLife 7, e32942 (2018).
Google Scholar
-
Wyler, E. et al. Single-cell RNA-sequencing of herpes simplex virus 1-infected cells connects NRF2 activation to an antiviral program. Nat. Commun. 10, 4878 (2019).
Google Scholar
-
Ratnasiri, K., Wilk, A. J., Lee, M. J., Khatri, P. & Blish, C. A. Single-cell RNA-Seq methods to interrogate virus–host interactions. Semin Immunopathol. 45, 71–89 (2023).
Google Scholar
-
Stoeckius, M. et al. Simultaneous epitope and transcriptome measurement in single cells. Nat. Methods 14, 865–868 (2017).
Google Scholar
-
Mulè, M. P., Martins, A. J . & Tsang, J. S. Normalizing and denoising protein expression data from droplet-based single cell profiling. Nat. Commun. 13, 2099 (2022).
Google Scholar
-
Singh, M. et al. High-throughput targeted long-read single cell sequencing reveals the clonal and transcriptional landscape of lymphocytes. Nat. Commun. 10, 3120 (2019).
Google Scholar
-
Ma, S. et al. Chromatin potential identified by shared single-cell profiling of RNA and chromatin. Cell 183, 1103–1116 (2020).
Google Scholar
-
Stephenson, E. et al. Single-cell multi-omics analysis of the immune response in COVID-19. Nat. Med. 27, 904–916 (2021).
Google Scholar
-
Wimmers, F. et al. The single-cell epigenomic and transcriptional landscape of immunity to influenza vaccination. Cell 184, 3915–3935 (2021).
Google Scholar
-
Dohmen, J. et al. Identifying tumor cells at the single-cell level using machine learning. Genome Biol. 23, 123 (2022).
Google Scholar
-
Cohen, E. M., Avital, N., Shamay, M. & Kobiler, O. Abortive herpes simplex virus infection of nonneuronal cells results in quiescent viral genomes that can reactivate. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 117, 635–640 (2020).
Google Scholar
-
Younan, P. et al. Ebola virus-mediated T-lymphocyte depletion is the result of an abortive infection. PLoS Pathog. 15, e1008068 (2019).
Google Scholar
-
Griffin, D. E. Why does viral RNA sometimes persist after recovery from acute infections? PLoS Biol. 20, e3001687 (2022).
Google Scholar
-
van den Elsen, K., Quek, J. P. & Luo, D. Molecular insights into the flavivirus replication complex. Viruses 13, 956 (2021).
Google Scholar
-
O’Neal, J. T. et al. West Nile virus-inclusive single-cell RNA sequencing reveals heterogeneity in the Type I interferon response within single cells. J. Virol. 93, e01778-18 (2019).
Google Scholar
-
Chung, H. et al. Joint single-cell measurements of nuclear proteins and RNA in vivo. Nat. Methods 18, 1204–1212 (2021).
Google Scholar
-
Bost, P. et al. Host-viral infection maps reveal signatures of severe COVID-19 patients. Cell 181, 1475–1488 (2020).
Google Scholar
-
Speranza, E. et al. Single-cell RNA sequencing reveals SARS-CoV-2 infection dynamics in lungs of African green monkeys. Sci. Transl. Med. 13, eabe8146 (2021).
Google Scholar
-
Kim, D. et al. The architecture of SARS-CoV-2 transcriptome. Cell 181, 914–921 (2020).
Google Scholar
-
Muhlberger, E. Filovirus replication and transcription. Future Virol. 2, 205–215 (2007).
Google Scholar
-
Solignat, M., Gay, B., Higgs, S., Briant, L. & Devaux, C. Replication cycle of chikungunya: a re-emerging arbovirus. Virology 393, 183–197 (2009).
Google Scholar
-
Grant, S. M., Lou, M., Yao, L., Germain, R. N. & Radtke, A. J. The lymph node at a glance—how spatial organization optimizes the immune response. J. Cell Sci. 133, jcs241828 (2020).
Google Scholar
-
Stoltzfus, C. R. et al. CytoMAP: a spatial analysis toolbox reveals features of myeloid cell organization in lymphoid tissues. Cell Rep. 31, 107523 (2020).
Google Scholar
-
Radtke, A. J. et al. A multi-scale, multiomic atlas of human normal and follicular lymphoma lymph nodes. Preprint at bioRxiv https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.06.03.494716 (2022).
-
Eng, J. et al. A framework for multiplex imaging optimization and reproducible analysis. Commun. Biol. 5, 438 (2022).
Google Scholar
-
Chen, H. Y., Palendira, U. & Feng, C. G. Navigating the cellular landscape in tissue: recent advances in defining the pathogenesis of human disease. Computational Struct. Biotechnol. J. 20, 5256–5263 (2022).
Google Scholar
-
Hickey, J. W. et al. Spatial mapping of protein composition and tissue organization: a primer for multiplexed antibody-based imaging. Nat. Methods 19, 284–295 (2022).
Google Scholar
-
Frederico, B., Chao, B., Lawler, C., May, J. S. & Stevenson, P. G. Subcapsular sinus macrophages limit acute gammaherpesvirus dissemination. J. Gen. Virol. 96, 2314–2327 (2015).
Google Scholar
-
Reynoso, G. V. et al. Zika virus spreads through infection of lymph node-resident macrophages. Cell Rep. 42, 112–126 (2023).
Google Scholar
-
Hickman, H. D. et al. Anatomically restricted synergistic antiviral activities of innate and adaptive immune cells in the skin. Cell Host Microbe 13, 155–168 (2013).
Google Scholar
-
Greenberg, A. et al. Quantification of viral and host biomarkers in the liver of rhesus macaques: a longitudinal study of Zaire Ebolavirus strain Kikwit (EBOV/Kik). Am. J. Pathol. 190, 1449–1460 (2020).
Google Scholar
-
Radtke, A. J. et al. IBEX: a versatile multiplex optical imaging approach for deep phenotyping and spatial analysis of cells in complex tissues. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 117, 33455–33465 (2020).
Google Scholar
-
Jiang, S. et al. Rhesus macaque CODEX multiplexed immunohistochemistry panel for studying immune responses during Ebola infection. Front. Immunol. 12, 729845 (2021).
Google Scholar
-
Rendeiro, A. F. et al. The spatial landscape of lung pathology during COVID-19 progression. Nature 593, 564–569 (2021).
Google Scholar
-
Berry, S. et al. Analysis of multispectral imaging with the AstroPath platform informs efficacy of PD-1 blockade. Science 372, eaba2609 (2021).
Google Scholar
-
Greenwald, N. F. et al. Whole-cell segmentation of tissue images with human-level performance using large-scale data annotation and deep learning. Nat. Biotechnol. 40, 555–565 (2022).
Google Scholar
-
Lee, M. Y. et al. CellSeg: a robust, pre-trained nucleus segmentation and pixel quantification software for highly multiplexed fluorescence images. BMC Bioinform. 23, 46 (2022).
Google Scholar
-
Method of the Year 2020: spatially resolved transcriptomics. Nat. Methods 18, 1 (2021).
-
Rao, A., Barkley, D., França, G. S. & Yanai, I. Exploring tissue architecture using spatial transcriptomics. Nature 596, 211–220 (2021).
Google Scholar
-
Moses, L. & Pachter, L. Museum of spatial transcriptomics. Nat. Methods 19, 534–546 (2022).
Google Scholar
-
Tian, L., Chen, F. & Macosko, E. Z. The expanding vistas of spatial transcriptomics. Nat. Biotechnol. 41, 773–782 (2022).
-
Acheampong, K. K. et al. Multiplexed detection of SARS-CoV-2 genomic and subgenomic RNA using in situ hybridization. Preprint at bioRxiv https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.08.11.455959 (2021).
-
Chen, K. H., Boettiger, A. N., Moffitt, J. R., Wang, S. & Zhuang, X. RNA imaging. Spatially resolved, highly multiplexed RNA profiling in single cells. Science 348, aaa6090 (2015).
Google Scholar
-
He, J. et al. In situ single-cell transcriptomic imaging in formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissues with MERSCOPE. Cancer Res. 83, 4195 (2023).
Google Scholar
-
Mantri, M. et al. Spatiotemporal transcriptomics reveals pathogenesis of viral myocarditis. Nat. Cardiovascular Res. 1, 946–960 (2022).
Google Scholar
-
Gracia Villacampa, E. et al. Genome-wide spatial expression profiling in formalin-fixed tissues. Cell Genomics 1, 100065 (2021).
Google Scholar
-
Kulasinghe, A. et al. Profiling of lung SARS-CoV-2 and influenza virus infection dissects virus-specific host responses and gene signatures. Eur. Respiratory J. 59, 2101881 (2022).
Google Scholar
-
Merritt, C. R. et al. Multiplex digital spatial profiling of proteins and RNA in fixed tissue. Nat. Biotechnol. 38, 586–599 (2020).
Google Scholar
-
Welch, J. D. et al. Single-cell multi-omic integration compares and contrasts features of brain cell identity. Cell 177, 1873–1887 (2019).
Google Scholar
-
Stuart, T. et al. Comprehensive integration of single-cell data. Cell 177, 1888–1902 (2019).
Google Scholar
-
Altboum, Z. et al. Digital cell quantification identifies global immune cell dynamics during influenza infection. Mol. Syst. Biol. 10, 720 (2014).
Google Scholar
-
Rooijers, K. et al. Simultaneous quantification of protein-DNA contacts and transcriptomes in single cells. Nat. Biotechnol. 37, 766–772 (2019).
Google Scholar
-
Xi, N. M. & Li, J. J. Benchmarking computational doublet-detection methods for single-cell RNA sequencing data. Cell Syst. 12, 176–194 (2021).
Google Scholar
-
Wang, F. et al. RNAscope: a novel in situ RNA analysis platform for formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues. J. Mol. Diagn. 14, 22–29 (2012).
Google Scholar
-
Radtke, A. J. et al. IBEX: an iterative immunolabeling and chemical bleaching method for high-content imaging of diverse tissues. Nat. Protoc. 17, 378–401 (2022).
Google Scholar
-
Black, S. et al. CODEX multiplexed tissue imaging with DNA-conjugated antibodies. Nat. Protoc. 16, 3802–3835 (2021).
Google Scholar
-
Goltsev, Y. et al. Deep profiling of mouse splenic architecture with CODEX multiplexed imaging. Cell 174, 968–981 (2018).
Google Scholar
-
Angelo, M. et al. Multiplexed ion beam imaging of human breast tumors. Nat. Med. 20, 436–442 (2014).
Google Scholar
-
Tsujikawa, T. et al. Quantitative multiplex immunohistochemistry reveals myeloid-inflamed tumor-immune complexity associated with poor prognosis. Cell Rep. 19, 203–217 (2017).
Google Scholar
-
Stack, E. C., Wang, C., Roman, K. A. & Hoyt, C. C. Multiplexed immunohistochemistry, imaging, and quantitation: a review, with an assessment of tyramide signal amplification, multispectral imaging and multiplex analysis. Methods 70, 46–58 (2014).
Google Scholar
-
Ståhl, P. et al. Visualization and analysis of gene expression in tissue sections by spatial transcriptomics. Science 353, 78–82 (2016).
Google Scholar
-
Christopher R. Merritt CR. et. al. High multiplex, digital spatial profiling of proteins and RNA in fixed tissue using genomic detection methods. Preprint at bioRxiv https://doi.org/10.1101/559021 (2019).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Cleveland Clinic Lerner Research Institute start-up funds.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The author declares no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Microbiology thanks Harshad Ingle, Stanley Lemon, Keir Balla, and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Reprints and Permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Speranza, E. Understanding virus–host interactions in tissues.
Nat Microbiol (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41564-023-01434-7
-
Received: 15 November 2022
-
Accepted: 20 June 2023
-
Published: 24 July 2023
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41564-023-01434-7