Infection
Live parasitic worm found in woman’s brain; know all about this parasitic infection
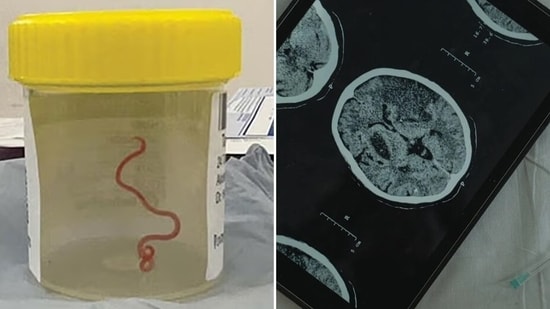
Doctors pulled out a live 8cm roundworm from the brain of a 64-year-old Australian woman who complained of forgetfulness and depression.
Parasites or worms are organisms that need other living organisms to survive and can cause various kinds of infections in human beings. Since parasites often live in intestine, the common symptoms of a parasitic infection are diarrhoea and vomiting apart from itchy skin rashes. Many infections also manifest in brain or lungs. From protozoa like amoeba, malaria, helminths that live in the intestines and can infect liver, lungs or brain, or Ectoparasites like mites, ticks, lice and flea, there are three main types of parasites that affect humans. Human brain is most common affected by Taenia solium – a pork tapeworm, causing a condition known as neurocysticercosis and Echinococcus – a tapeworm, causing hydatid disease. (Also read: World’s first case of live parasitic worm found in Australian woman’s brain: ‘Alive and wriggling’)
Doctors pulled out a live 8cm roundworm from the brain of a 64-year-old Australian woman who complained of forgetfulness and depression. The lady also suffered from symptoms like abdominal pain and diarrhoea, constant dry cough, fever and night sweats a year back. Doctors suspected some kind of infection in the brain, but never expected they would find an alive and wriggling worm.
“The 64-year-old Australian woman was infected by a rare parasite called Ophidascaris Robertsi. This is a type of Roundworm (Helminth). This roundworm usually lives in a Carpet Python called Morelia Spilota. The eggs of the worm are around the snakes’ faecal droppings, which infect the grass. This grass containing the eggs, are eaten by small mammals, who are then eaten by the Carpet Python. This is how this worm gets cycled between its two hosts. This woman became an ‘accidental host’. She lived near the carpet python habitat and while foraging the native vegetation for cooking, she ingested the egg. The worm developed in her intestine and travelled via blood circulation to her brain. It caused symptoms of forgetfulness, confusion and headache. Upon consulting the doctors, she underwent an MRI brain scan, which showed inflammation in the area of the brain with an underlying parasite. She underwent surgery,” says Dr Himanshi Champaneri, Senior Consultant – Department of Neurosurgery, Marengo Asia Hospitals, Gurugram.
Symptoms of parasitic infection in brain
“These organisms reach the brain via blood circulation and start growing there. In response, the body produces inflammation around the worm and as a result, an area of inflammatory tissue or granuloma develops in the brain. Depending upon the affected location, it can cause a multitude of symptoms such as pressure symptoms – headache, vomiting, visual blurring, confusion, altered sensorium, cognitive symptoms – forgetfulness, problems in understanding, calculations, disorientation, seizures and epilepsy – due to irritation of the brain by inflammatory tissue, and circulation block – it can block the normal circulation of brain fluid and cause sudden increase in fluid pressures called hydrocephalus. Without treatment, these conditions can be fatal and patients can die,” says Dr Himanshi.
Who are at risk?
Human population living in close vicinity to the animals or forest are likely to get infected by these parasites:
- People eating raw vegetables, uncooked food, are likely to consume the parasitic eggs.
- Partially or poorly cooked meat of animals such as dog, cow, pigs etc. when consumed, can lead to direct entry of these worms inside the human. Most of the people living with pets can encounter parasitic eggs in the pets faces.
How to prevent this infection
- Proper washing of all vegetables before consuming
- Purchasing meat from an authentic source and cooking it properly to kill the underlying parasites
- Deworming of pets at regular intervals
- Frequent hand washing after every outing from the house, if you are living in a forest or similar areas
Phases, complications and treatment of parasitic infection
Dr Himanshi explains how this infection begins, complications arising out of it and how it is treated.
Intestinal phase: When the eggs are consumed and parasites grow in the intestine, they cause abdominal cramps, diarrhoea, loss of appetite, nausea and asymptomatic period. This is the phase when the worms are growing in the intestine and the body is not responding with any active defence.
Neurologic phase: When the worms have reached the target organ, the brain, they can cause symptoms such as headache, confusion, forgetfulness, seizures, altered sensorium and sometimes death.
Complications
- It can cause epilepsy, with is a disorder of multiple frequent unprovoked seizures.
- Encephalopathy: It can cause damage to the brain leading to decline in cognition and progressive deterioration of the mental functions
- Hydrocephalus: It can cause obstruction to fluid circulation pathways, needing urgent surgery for fluid diversion.
- Coma and death
Treatment
“The parasitic infections are treatable with anthelminthics drugs. Brain infections often need surgery for the removal of parasite, reduction of the pressure and sometimes fluid diversion via shunt procedure. The surgery is frequently done via a keyhole and using endoscope or operating microscope,” says Dr Himanshi.