Blood, Health Care, Symptoms
High Bilirubin Levels
The breakdown of red blood cells results in the production of a chemical called bilirubin, which has a yellowish color. It is typically eliminated from the body via the fluid known as bile, which is produced by the liver. On the other hand, if the liver is damaged, it is possible that it will not be able to eliminate bilirubin as effectively. This might result in an accumulation of bilirubin in the blood, which can induce jaundice, which is characterized by a yellowing of the skin as well as the eyes.
A blood test for bilirubin can assist medical professionals in determining the concentration of bilirubin currently present in the blood. This may be used as a screening tool for liver impairment as well as other disorders that lie beneath the surface.
Normal vs. High Bilirubin Levels
In a healthy individual, the level of bilirubin in their blood should be lower than one milligram per deciliter (mg/dL). The bilirubin level at this point is considered to be normal. The condition known as hyperbilirubinemia occurs when the concentration of bilirubin in the blood is more than 1 mg/dL. Getting checked out by a doctor is typically necessary while dealing with this disease.
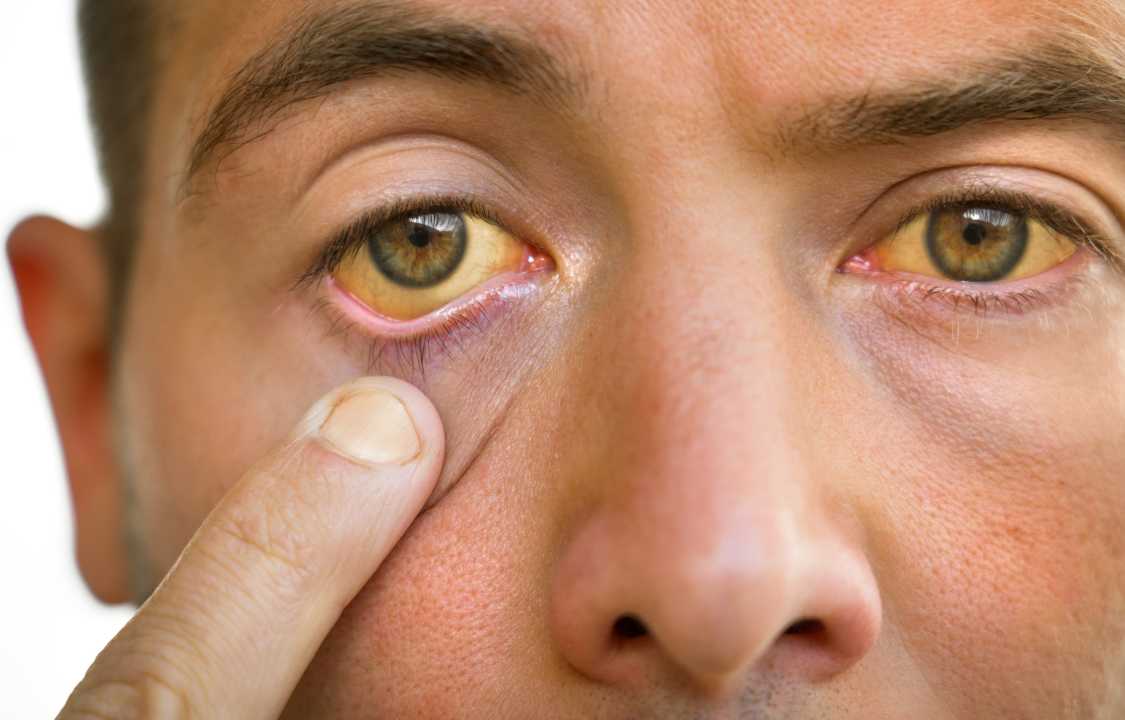
Jaundice is a condition that can be caused by hyperbilirubinemia. Jaundice is characterized by a yellowing of the skin and the eyes. The development of jaundice is one of the most prominent symptoms of hyperbilirubinemia. When there is 3 mg/dL of bilirubin in the blood, the whites of the eyes will begin to become yellow. This happens because bilirubin is a waste product. As the quantity of bilirubin in the blood continues to rise, the color of the skin will begin to change to a yellowish hue as well. There is a possibility that the skin will turn a lemon yellow tint.
Bilirubin Levels in Newborns
It is not abnormal for the amount of bilirubin in a baby to be somewhat elevated. This is due to the fact that the baby’s liver has not yet reached the stage of maturity required to filter out the excessive bilirubin from the blood. Jaundice, characterized by a yellowing of the skin and eyes, can affect around sixty percent of newborns. The jaundice, on the other hand, will often go on its own during the first couple of weeks and will not result in any difficulties.
In the event that your infant has jaundice, your pediatrician will likely do additional tests in order to identify the underlying reason. This is due to the fact that having high amounts of bilirubin might be an indicator of various health issues, including liver damage.
Here are some additional things to keep in mind about jaundice in newborns:
- The jaundice is usually most noticeable on the face, chest, and abdomen.
- The baby’s skin may also feel warm and clammy.
- The baby’s stool may be pale or clay-colored.
- The baby’s urine may be dark yellow or orange.
What Can Cause Your Bilirubin Levels to Be High?
Your doctor may order more exams and inquire about other symptoms in order to pin down the root cause of your elevated bilirubin levels. In many medical situations, elevated bilirubin levels may develop.
- Hepatitis
Inflammation of the liver, often known as hepatitis, is typically caused by a virus. The liver’s inflamed state may prevent it from eliminating bilirubin effectively. As a result, those with hepatitis may have fluctuating amounts of bilirubin in their blood. Symptoms of hepatitis are uncommon. In addition to jaundice caused by a rise in bilirubin, other symptoms of hepatitis include a high body temperature, weakness, lack of appetite, nausea, vomiting, and stomach discomfort.
- Cirrhosis
Scarring of the liver tissue is known as cirrhosis. Several disorders, including chronic hepatitis, can damage the liver over time, eventually leading to cirrhosis. Persistently elevated bilirubin levels have been linked to cirrhosis and other forms of serious liver disease.
- Liver damage caused by alcohol abuse
Damage to the liver, such as hepatitis, cirrhosis, and fatty liver disease, can be caused by heavy and chronic alcohol intake. If your liver is damaged, it may not be able to flush bilirubin out of your system, leading to dangerously high concentrations of the substance in your blood. In the case of alcohol-induced hepatitis, for instance, bilirubin levels might be higher than 5mg/dL.
- Anaemia Hemolytica
Hemolytic anemia is characterized by an abnormally rapid breakdown of red blood cells. Increased RBC breakdown results in a higher bilirubin concentration. Therefore, jaundice can be a symptom of hemolytic anemia. Weakness and dizziness are other symptoms of the blood disease.
- Gallstones
The gallbladder is a pouch in which bile is stored, and gallstones are hard lumps that develop there. Blockage of the bile ducts by gallstones is a common cause of hyperbilirubinemia. Gallstones can also cause discomfort, nausea, vomiting, and fever in addition to jaundice.
- Syndrome of Gilbert
Gilbert syndrome is a common inherited condition that disrupts bilirubin metabolism in the liver. An increased bilirubin level, often less than 2mg/dL, is a possible symptom of the illness. Tiredness is a possible symptom of Gilbert syndrome. Mild jaundice is also possible, especially when they:
- Are exerting themselves
- are anxious
- Get a disease
- Not eating
Symptoms of High Bilirubin Levels
When bilirubin levels are too high, jaundice is the first symptom that occurs. It’s possible that the whites of the eyes will get darkened initially. When the amounts of bilirubin reach even greater levels, the skin takes on a yellowish tinge and may even become totally green if the condition is severe enough.
The yellowing of the skin may be less noticeable in those who have darker complexions. To properly diagnose jaundice in some patients, it is necessary to look for further color changes throughout the body. In addition to the eyes, you should also look for changes in the color of the gums and the insides of the lips. Other signs of jaundice include the following:
- Urine that is a dark brown or black
- Stools that are pale or a clay hue
- Itching
It is possible that you will also have additional symptoms, but this will depend on the cause of your excessive bilirubin levels. In some circumstances, an increase in bilirubin level is achievable without any apparent negative effects on one’s health.
Symptoms of High Bilirubin Levels in Babies
Jaundice is a common symptom that manifests itself in newborns with high bilirubin levels. As jaundice spreads, the skin on the face is typically the first to go yellow, followed by the chest, belly, arms, and legs of the affected individual. Infants frequently also have yellowing of the whites of their eyes.
High bilirubin levels in an infant can manifest in a variety of ways, not only jaundice:
- Having trouble falling asleep and waking up
- not a good baby at nursing or bottle feeding
- Making a fuss
- Not having at least three solid stools per day and four wet diapers per day by the fourth day
Testing Bilirubin Levels
If your physician suspects that you have a liver condition, he or she may suggest that you undergo a bilirubin test. A test for bilirubin can identify an increased amount of this substance, which can be an indicator of liver disease. In certain cases, a blood sample is necessary for the test, but in other cases, a sample of urine can be used instead. When drawing blood from a vein in the arm, a very fine needle is the instrument of choice.
It’s possible that you’ve got some kind of liver injury if your bilirubin levels are excessively high. But there are times when that is not the case. Bilirubin levels can also be raised by the use of some medications, as well as by certain types of physical activity and dietary choices.
Your doctor may advise you to undergo further tests, such as a test of your urine and liver function, as well as an ultrasound, in order to assist in determining the underlying reason for your abnormally high bilirubin levels.
Testing Bilirubin Levels in Babies
Kernicterus is a form of brain injury that can be caused when bilirubin levels remain abnormally high for an extended period of time. Most babies have higher levels of bilirubin, but these levels eventually return to normal on their own. Kernicterus can cause hearing loss, as well as issues with eyesight and teeth, in addition to other complications.
During the first two days of a baby’s life, healthcare professionals should check for jaundice between every eight and 12 hours to avoid this from happening. The newborn should then undergo a second round of testing between the ages of three and five days old, as this is the age range in which a baby’s bilirubin level is normally at its maximum.
Light therapy or phototherapy is utilized by medical professionals in the treatment of jaundice in infants. In order to do this, the infant is illuminated by specialized lighting designed to lower the baby’s bilirubin levels.