Infection
Changes in Group A Streptococcus emm Types Associated with Invasive Infections in Adults, Spain, 2023
Disclaimer: Early release articles are not considered as final versions. Any changes will be reflected in the online version in the month the article is officially released.
Author affiliations: Hospital Universitari Arnau de Vilanova, Lleida, Spain (A. Bellés-Bellés, N. Prim, S. Mormeneo, A. Jover-Sáenz, N. Aixalà, A. Bernet, É. López-González, I. Prats, M. García-González); Institut de Recerca Biomèdica de Lleida, Lleida (A. Bellés-Bellés, N. Prim, S. Mormeneo, A. Jover-Sáenz, A. Bernet, É. López-González, I. Prats, M. García-González); Centro Nacional de Microbiología, Instituto de Salud Carlos III, Madrid, Spain (P. Villalón-Panzano, M. Valiente-Novill)
Streptococcus pyogenes (group A Streptococcus [GAS]) can cause a broad range of infections. Although usually associated with streptococcal pharyngitis and skin and soft tissue infections, GAS can also cause life-threatening infections, such as sepsis or necrotizing fasciitis (1).
In December 2022, the World Health Organization issued an alert about increasing rates of invasive GAS (iGAS) infections in children in Europe (2). This warning was followed by a health advisory from the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention that reported an increase in these infections among children in the United States (3). Since then, several countries in Europe have notified an increase, particularly in the pediatric population (4).
A total of 31 culture-confirmed iGAS cases (incidence 0.0912 cases/1,000 inhabitants) were detected during November 2022–May 2023 in the province of Lleida (catchment of 340,000 inhabitants) in northeast Spain. Invasive cases were defined according to Centers for Disease Control and Prevention definitions (5). The median age was 62 years (range 3–93 years); 4 cases occurred in children. Three deaths in adults were notified during this period. Given that increase, we analyzed the distribution of iGAS in Lleida province during January 2011–May 2023 (Appendix Figure). The average number of iGAS cases per year was 5.2 (incidence 0.0153 cases/1,000 inhabitants/year) during 2011–2018. A total of 19 culture-confirmed cases (incidence of 0.0559 cases/1,000 inhabitants/year) were reported in 2019, followed by a decline in incidence during the COVID-19 pandemic (0.0162 cases/1,000 inhabitants/year). The increase detected since November 2022 surpassed 2019 incidence.
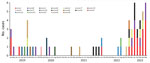
Hospital Universitari Arnau de Vilanova (Lleida, Spain) began participating in the iGAS national surveillance program in April 2019. Conducted at Centro Nacional de Microbiología (Majadahonda, Spain), this program performs emm typing and toxin gene profiling of iGAS isolates collected from microbiology laboratories. We analyzed the monthly distribution of emm types involved in 61 iGAS cases reported during January 2019–May 2023 in our geographic area (Figure). Overall, 19 different emm types were detected; emm1 (n = 18/61) was the most frequent, followed by emm49 (n = 8/61) and emm89 (n = 8/61). A decrease in type diversity was observed since November 2022; the 6 emm types detected were emm1 (n = 15/31), emm12 (n = 5/31), emm49 (n = 5/31), emm89 (n = 4/31), emm77 (n = 1/31) and emm58 (n = 1/31) (Table).
A large increase in iGAS was detected beginning in November 2022. Decreased exposure to GAS during the COVID-19 pandemic because of mask use and social isolation might have contributed to its low circulation. The decline of masking and social distancing, combined with high rates of respiratory viruses during the winter of 2021–2022, might be behind the increase in iGAS. We found that most iGAS occurred in adults and had a low mortality rate, in contrast with previous reports (4).
Certain GAS emm types have been strongly associated with invasive infections. However, a notorious geographic diversity in the circulation of emm types exists (7). The most common types involved in iGAS in Spain from 2007–2019 were emm1, emm89, and emm3, according to the GAS Surveillance Program in Spain. In contrast, only 1 emm49 isolate was detected during that period (6). In our study, emm1 was predominant in accordance with other reports in Europe (4). After emm1, emm49 and emm89 were the most frequent emm types in our study. A substantial expansion of emm49 has been recently reported in United States, where it represents the third most common emm type associated with iGAS, after emm1 and emm89 (8). However, emm49 was an unusual emm type in northeast Spain until recently and was rarely involved in iGAS in Europe (4,9). After emm49 was first detected in the nationwide surveillance program in Spain in 2011, circulation increased in Spain during 2021–2023 (P. Villalón-Panzano, unpub. data). Including our 8 cases, 11 emm49 iGAS cases were notified by this program during this period. Despite the lack of a clear epidemiologic link, an outbreak could not be ruled out in this area. The first detection of emm49 iGAS in Lleida province was in October 2021. The main clinical manifestations of iGAS associated with emm49 were skin and soft tissue infections, as previously described (8).
A high incidence of iGAS in children during 2019 was recently reported in Spain (10). Our data showed an increasing trend of iGAS in adults in our area that was interrupted by the COVID-19 pandemic. Together with an accumulation of iGAS, a decline in emm type diversity has been detected since the World Health Organization alert in late 2022.
In conclusion, this report supports that the increase in iGAS in adults probably began before the COVID-19 pandemic in northeast Spain. The postpandemic increase was caused by a limited number of emm types. Although emm1 was the most common type, emm49 is an emergent cause of iGAS in Europe. Continuous surveillance is essential to detect the emergence and spread of emm types associated with iGAS in different geographic areas.
Dr. Bellés-Bellés is a clinical microbiologist at the Hospital Universitari Arnau de Vilanova de Lleida (Spain) and the Head of the Research Group in Clinical Microbiology at the Biomedical Research Institute (IRBLleida). Her primary research interest are bacterial infections and antibiotic resistance.
Top
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors’ affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.