Health Care, Insight
Hydrogen Peroxide for Ear Wax Removal: What To Know
Experts weigh in on the ear wax removal method.
Ear wax, scientifically known as cerumen, is a naturally occurring and protective substance within the ears. It is secreted by specialized glands in the ear canal and serves several essential functions, such as trapping dust and foreign particles, lubricating the ear canal, and preventing infections. While the ears possess mechanisms for self-cleaning, individuals may occasionally feel the need to remove excess ear wax due to discomfort, reduced hearing, or other reasons. This desire for ear wax removal often leads to various methods, with one popular option being the use of hydrogen peroxide.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the safe and effective use of hydrogen peroxide for ear wax removal, offering insights into its application, safety considerations, and when it is prudent to consult a healthcare provider. It’s important to note that while hydrogen peroxide can be a useful tool for ear wax removal, improper use can lead to complications, including ear infections and damage to the delicate structures of the ear. Therefore, it is crucial to follow the recommended guidelines and exercise caution when attempting to clean your ears at home.
The Science of Ear Wax Removal: Hydrogen Peroxide and TikTok Sensations
In August 2021, TikTok user Ayisha Friedman-Negrín (@ayishafrita) garnered millions of likes for their viral video demonstrating the use of hydrogen peroxide for ear cleaning. The video showcased a technique that was perceived as effective in “properly cleaning ur ears.”
In the video, Friedman-Negrín lay their head down on a towel with one ear facing upward, administered a few drops of hydrogen peroxide into their ear, and observed the ensuing reaction. “It’s going to just bubble in there,” they explained. “It basically is just separating all the earwax, and then I’m going to flip, and it’s all going to come out.” The process was repeated for the other ear after the bubbling had subsided.
This TikTok sensation raised questions about the safe and correct utilization of hydrogen peroxide for ear wax removal.
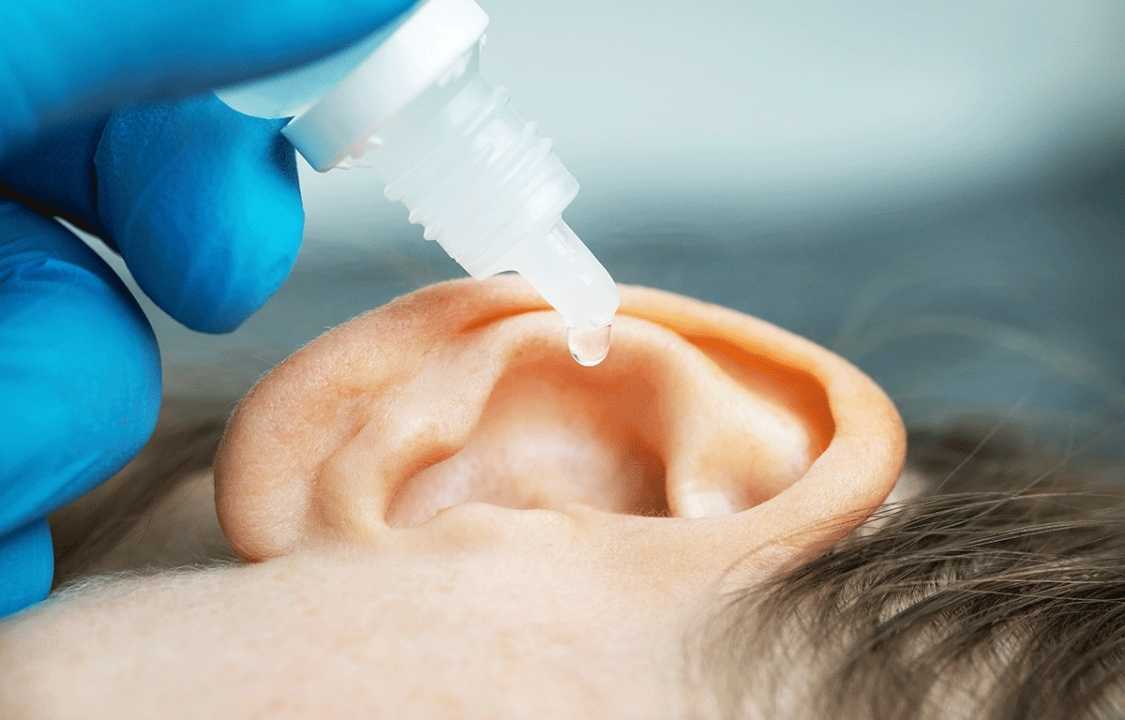
Safely Using Hydrogen Peroxide: A Step-by-Step Guide
For individuals with healthy ears who wish to explore this ear wax removal method, it is crucial to follow a safe procedure. Dr. John Dobrowski, an ear, nose, and throat physician at Mass Eye and Ear and instructor of otolaryngology–head and neck surgery at Harvard Medical School, provides the following guidelines:
1. Dilution: Create a mixture that consists of equal parts hydrogen peroxide and water. This dilution helps mitigate any potential abrasiveness on the delicate ear canal.
2. Temperature: Ensure that the solution is close to body temperature, as excessively cold or warm solutions may induce dizziness.
3. Application: Utilize a dropper to administer a small amount of the diluted hydrogen peroxide into the ear.
4. Waiting Time: Allow the solution to sit in the ear for approximately 10 seconds.
5. Drainage: After the waiting period, gently tilt your head to let the solution drain out.
Crucially, post-procedure care is equally important. Dr. Dobrowski emphasizes the necessity of thoroughly drying the ear after hydrogen peroxide use. A damp environment within the ear canal can potentially lead to otomycosis or fungal infections, underscoring the importance of proper aftercare.
How Often Should You Remove Earwax?
In most cases, earwax does not require regular removal. The ears are remarkably adept at self-cleaning, and their intricate mechanisms work diligently to maintain ear health. Earwax, scientifically known as cerumen, is a remarkable substance that naturally oozes or gradually falls out of the ear over time. This gradual exodus of earwax is a part of the body’s intricate self-maintenance system, ensuring the ears remain clear and functional.
The self-cleaning process is not limited to the natural migration of earwax. It also involves the movement of tiny hairs (cilia) within the ear canal, which help to transport debris, dust, and earwax from the deep ear canal to the outer ear, where it can be easily wiped away during regular hygiene routines like showering. The warm water and steam from a shower can further facilitate the removal of earwax, as it helps to soften the cerumen and encourage its gentle expulsion from the ear.
The multifaceted function of earwax extends beyond simple protection—it serves as a guardian of the ear’s well-being. This remarkable substance acts as a formidable barrier, preventing dust, germs, and foreign objects from infiltrating the delicate and sensitive skin within the ear canal. It is a testament to the body’s ingenious design, providing a defense mechanism that keeps the ears safe and sound.
According to Dr. Scott B. Shapiro, an esteemed ear, nose, and throat specialist at Rutgers Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, routine ear cleaning is generally unnecessary for most individuals. The human body’s natural processes are typically sufficient to maintain ear health. Interventions for ear cleaning should be considered primarily when individuals experience hearing difficulties, discomfort, or are genuinely bothered by the presence of excess earwax. In such cases, seeking guidance from a healthcare provider is advisable, as they can provide appropriate recommendations and, if necessary, perform safe and effective earwax removal procedures. It is important to exercise prudence and prioritize the preservation of ear health by only intervening when it is truly warranted.
Risks and Safety Considerations
While hydrogen peroxide can be a useful tool for ear wax removal, there are specific risks and safety considerations to bear in mind:
1. Avoidance in Certain Cases: Hydrogen peroxide should not be used in cases where individuals are experiencing infections, pain, or have a perforated eardrum, as it may exacerbate these conditions.
2. Skin Irritation: Regular-strength hydrogen peroxide has the potential to irritate the ear canal skin and eardrum. It is advisable to exercise caution and use gentle solutions.
When to Seek Professional Advice
In certain situations, ear wax removal may necessitate professional assistance. If individuals encounter blocked earwax and experience any of the following symptoms, it is advisable to consult a healthcare provider:
- Ear drainage or pain.
- Fever.
- Persistent hearing loss following earwax removal attempts.
Additionally, it is crucial for individuals who find themselves frequently attempting at-home ear cleaning to consider consulting an ear, nose, and throat specialist, known as an otolaryngologist. These highly trained specialists can thoroughly assess the ear’s condition and provide appropriate guidance and treatment options. This may include prescribing specialized lotions, drops, or steroid oils to effectively address any crusting, flaking, or other ear-related concerns.
In summary, while hydrogen peroxide can be safely employed for earwax removal when done correctly and in specific situations, it’s important to exercise caution. Earwax management is typically a self-regulating process, and professional consultation is strongly recommended when experiencing persistent ear-related issues or excessive at-home cleaning practices. Ultimately, maintaining a balanced approach to ear hygiene and health is essential for ensuring optimal ear well-being and preventing potential complications.