Chronic, Disease, Health Care, Insight
Why Your Weight Matters If You Have Psoriasis
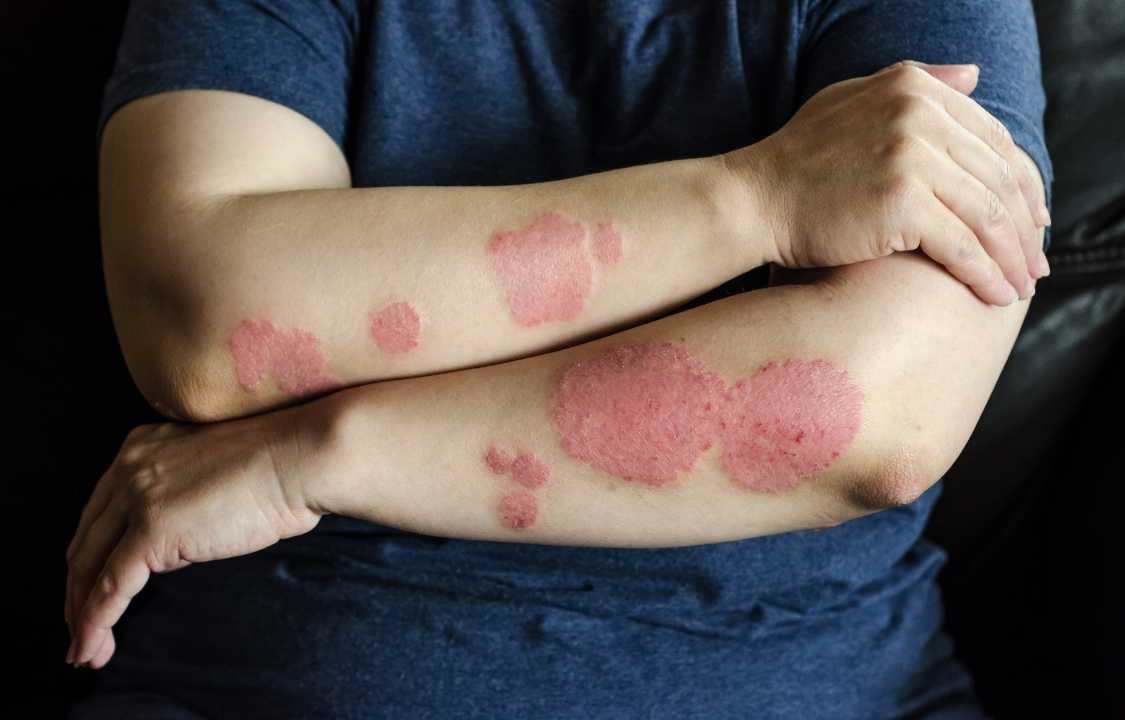
If you have the skin condition psoriasis, keeping extra pounds off could make a big difference in your symptoms.
Losing weight is a pivotal and often underestimated aspect of managing psoriasis, an autoimmune skin condition characterized by raised red, white, or silvery patches on the skin, accompanied by various symptoms such as itching, nail abnormalities, and dry, cracked skin. While lifestyle strategies like stress management, gentle skincare, and dietary choices play essential roles in psoriasis management, the impact of shedding extra pounds on this chronic condition is a subject of paramount importance. In this comprehensive exploration, we delve into five compelling reasons why weight management is crucial for individuals grappling with psoriasis.
1. Symptom Improvement through Weight Loss
Psoriasis is an autoimmune ailment wherein the body’s immune system targets the skin. However, recent studies have illuminated the connection between lifestyle factors, including weight, and the severity of psoriasis symptoms. Dr. Debra Jaliman, a distinguished dermatologist in New York City, underscores the significance of diet and exercise in reducing psoriasis symptoms. A noteworthy Danish study published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition corroborates this notion, revealing that obese psoriasis sufferers who lost 10% to 15% of their body weight witnessed a marked improvement in their condition. Impressively, these positive changes persisted even a year after the study concluded, demonstrating the enduring benefits of weight loss.
2. Reducing the Risk of Psoriatic Arthritis
Psoriatic arthritis, an autoimmune disease characterized by painful and swollen joints, afflicts 10% to 30% of psoriasis patients. It has been observed that overweight or obese individuals with psoriasis are at a heightened risk of developing this debilitating condition. A comprehensive study spanning 15 years and encompassing over 75,000 subjects in the UK, published in the Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, established a clear association between obesity and the incidence of psoriatic arthritis. As body mass index (BMI) increased, so did the likelihood of developing this comorbid condition.
3. Alleviating Psoriatic Arthritis Symptoms
For individuals grappling with both psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis, excess weight can exacerbate joint-related discomfort significantly. Psoriatic arthritis affects joints of varying sizes, from small ones like fingers and toes to weight-bearing ones such as knees and hips. The added burden of surplus pounds places undue strain on these joints, intensifying the symptoms and diminishing overall mobility. Dr. James R. O’Dell, Chief of Rheumatology at the University of Nebraska Medical Center, emphasizes the adverse impact of excess weight on weight-bearing joints, particularly hips and knees, as it not only increases pain but also hampers joint function and flexibility.
A 2014 study conducted by Canadian researchers substantiates this claim, revealing that obese psoriatic arthritis patients were less likely to achieve remission compared to those with lower BMIs. This finding underscores the intricate relationship between body weight and disease progression in individuals with psoriatic arthritis. Moreover, the study highlights the need for personalized treatment plans that consider weight management as an essential component to optimize outcomes for these patients.
In light of these findings, healthcare providers are increasingly recognizing the importance of addressing weight management as part of the holistic care approach for psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis patients. This approach involves not only medical treatment but also lifestyle modifications, including dietary changes and exercise regimens tailored to each individual’s needs and capabilities. By actively managing their weight, patients can potentially reduce the severity of their symptoms, improve joint function, and enhance their overall quality of life.
4. Enhancing Medication Efficacy
Obesity can hinder the effectiveness of medications prescribed to manage psoriatic arthritis and psoriasis. The Arthritis Foundation highlights that overweight and obese individuals often respond less favorably to the drugs employed for treating these conditions. Dr. O’Dell explains this phenomenon as a “perfect storm” where weight-related issues not only increase the likelihood of medication-related complications but also reduce the medication’s efficacy. Research has shown that losing weight can improve the performance of biologic drug treatments, offering a ray of hope for individuals battling these autoimmune diseases.
5. Reducing the Risk of Comorbid Diseases
Beyond the confines of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis, weight management holds broader health implications. Shedding excess pounds can lower the risk of developing conditions like heart disease, diabetes, and stroke—conditions for which psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis patients are at an elevated risk. Dr. O’Dell underscores the importance of maintaining a healthy body weight, particularly for individuals with these autoimmune conditions. Weight loss, he asserts, is doubly significant for them, as it not only mitigates the burden of their primary ailment but also mitigates the risk of associated comorbidities.
Furthermore, Dr. O’Dell emphasizes that addressing weight management should be integrated into the overall treatment plan for psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. It’s not just about aesthetics but about improving overall health and reducing the strain on the body. Achieving and maintaining a healthy body weight can enhance the effectiveness of medical interventions and medications used to manage these conditions.
In addition to the physical benefits, weight management can also have a positive impact on a person’s mental well-being. As individuals with psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis often face challenges related to their appearance and physical discomfort, successful weight management can boost their self-esteem and quality of life.
Dr. O’Dell suggests that a multidisciplinary approach to weight management, involving healthcare professionals such as nutritionists, physical therapists, and mental health counselors, can provide individuals with psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis the comprehensive support they need on their journey towards better health.
In conclusion, the imperative of weight management in the context of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis cannot be overstated. It is a multifaceted strategy that not only alleviates the severity of symptoms but also reduces the risk of comorbid conditions and enhances the effectiveness of treatment modalities. By shedding extra pounds, individuals afflicted with these autoimmune diseases can take substantial steps toward achieving an improved quality of life and overall well-being. Therefore, integrating weight management into the comprehensive care plan for psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis is not merely a choice but a necessity—a holistic approach to health, vitality, and long-term wellness. This integrated approach not only addresses the physical aspects but also fosters psychological and emotional well-being, leading to a more balanced and fulfilling life. In essence, weight management becomes a cornerstone in the foundation of a healthier and happier existence for those dealing with these chronic conditions.