Health Care
What Causes A Swollen Uvula?
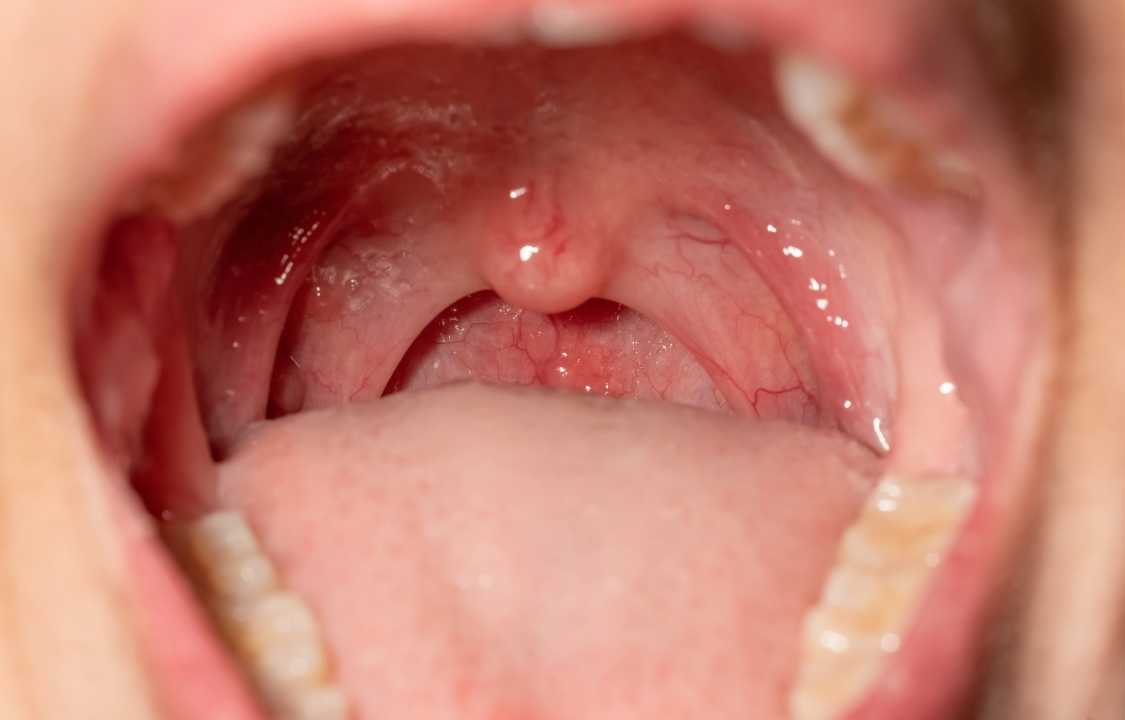
The uvula, that teardrop-shaped piece of tissue hanging at the back of your throat, plays a vital role in your oral and throat health. As a component of the soft palate, it contributes to the secretion of saliva, which moistens your mouth and throat. Moreover, it aids in the propulsion of food from your mouth to your throat, facilitating the swallowing process. However, like any other part of your body, the uvula can experience inflammation, a condition known as uvulitis. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore uvulitis in detail, including its causes, symptoms, treatment options, and frequently asked questions.
Symptoms of Uvulitis
Uvulitis manifests when the uvula becomes inflamed or swollen. Inflammation is a natural response of the immune system to various triggers, such as infections, allergies, or injuries. When your uvula is inflamed, you may experience several symptoms, including:
1. Itchiness or Discomfort: A persistent itching or discomfort sensation in the throat may be an early sign of uvulitis.
2. Redness: The uvula may appear red and inflamed, indicating the presence of inflammation.
3. Swelling: Swelling of the uvula is a characteristic symptom of uvulitis. The uvula may become enlarged and hang down noticeably.
4. Burning Sensation: Some individuals with uvulitis report a burning sensation in the throat, adding to their discomfort.
5. Feeling of a Foreign Object: Uvulitis can give the sensation of a foreign object or lump in the back of the throat.
6. Trouble Swallowing: Swelling in the throat may lead to difficulty swallowing, which can be uncomfortable and distressing.
According to a case study published in the IDCases, additional symptoms of uvulitis can include:
- Swollen tonsils
- Difficulty breathing
- Pain
- Sore throat
- Coughing
- Fever
- Nasal regurgitation
- Excessive saliva
- Painful or difficult swallowing
- Gagging
Causes of Uvulitis
Uvulitis can have various causes, with infections, allergies, and trauma being common triggers. While the exact cause may remain unknown in some cases, several factors can contribute to the development of uvulitis:
1. Infections: Bacterial and viral infections are frequent culprits of uvulitis. Infections that may lead to uvulitis include the common cold, flu, strep throat, and even COVID-19.
2. Genetics: Certain genetic traits, such as a cleft lip or palate, can make individuals more susceptible to developing a swollen uvula.
3. Allergies: Allergies, particularly severe allergic reactions, can trigger swelling in the mouth and throat, a condition known as isolated uvular angioedema or Quincke’s disease. Allergens like foods and insect bites can provoke this response, and severe cases may require immediate medical attention.
4. Smoking: Smoking and exposure to irritants from tobacco can irritate the tissues in the mouth and throat, potentially including the uvula.
5. Pollutants: Airborne chemicals and pollutants can also irritate the mouth and throat, leading to uvulitis. Common irritants include volatile organic compounds, carbon monoxide, and radon, as identified by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA).
6. Trauma: Trauma or injury to the mouth and throat can result in irritation and subsequent swelling of the uvula. Potential causes of injury may include acid reflux or endoscopic procedures.
Treatment Options for Uvulitis
When faced with symptoms of uvulitis, it is advisable to seek medical attention to diagnose the underlying cause. Healthcare providers will typically follow a series of steps to determine the source of your symptoms:
1. Medical History: Your healthcare provider will inquire about your personal and family medical history, including any relevant allergies or previous incidents of uvulitis.
2. Symptom Assessment: You will be asked to describe your current symptoms, including their onset, severity, and any associated discomfort.
3. Lifestyle Factors: Discussion of lifestyle factors, such as smoking or exposure to potential irritants, can provide valuable insights into the potential cause of uvulitis.
4. Physical Examination: A physical examination may involve inspecting the throat and uvula, taking a throat swab, or conducting blood tests to identify potential infections.
Once the underlying cause of uvulitis is determined, treatment options can be explored. Treatment may vary based on the cause and severity of the condition:
- Antiviral Medications: In cases where viral infections, such as severe colds, the flu, or COVID-19, are responsible for uvulitis, antiviral medications may be prescribed.
- Antibiotics: Bacterial infections, including strep throat, may require treatment with antibiotics to address the root cause of uvulitis.
- Epinephrine (Epipen): For severe allergic reactions that could be life-threatening, healthcare providers may prescribe emergency epinephrine to counteract the allergic response.
Home Remedies for Uvulitis
In some instances, mild cases of uvulitis can be managed with home remedies to alleviate symptoms and promote healing. These home remedies include:
1. Ice Consumption: Sucking or chewing on ice can help reduce swelling and provide relief.
2. Saltwater Gargling: Gargling with warm salt water can alleviate discomfort and reduce swelling.
3. Hydration: Staying well-hydrated by drinking plenty of fluids can keep the throat moist and promote healing.
4. Rest: Adequate rest is crucial to support the body’s recovery from infections that contribute to uvulitis.
5. Herbal Tea with Honey: Drinking hot herbal tea with honey can soothe throat pain and discomfort.
6. Allergen Avoidance: Identifying and avoiding allergens and irritants, such as pollen and smoke, can prevent exacerbation of uvulitis.
7. Throat Lozenges: Over-the-counter throat lozenges can provide temporary relief by soothing the throat.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Is a Swollen Uvula Serious?
In general, a swollen uvula is not a severe medical condition, but it can cause discomfort and potentially obstruct the airway. Although it is unlikely to cause long-term harm or be fatal, it is advisable to consult a healthcare provider if you experience swelling, as it may indicate an underlying condition like the flu or COVID-19.
How Long Does a Swollen Uvula Last?
The duration of a swollen uvula typically correlates with the resolution of the underlying cause. If it is due to an allergy, it may clear within a few days. In cases where a cold or infection is the culprit, improvement is expected as you recover from the illness.
Why Did I Wake Up With a Swollen Uvula?
Waking up with a swollen uvula could result from various factors, including trying a new food to which you may be allergic. Other potential causes may involve exposure to irritants or the onset of an infection, such as a cold.
Conclusion
In summary, uvulitis, characterized by the inflammation and swelling of the uvula, can be triggered by a range of factors, including infections, allergies, and trauma. While a swollen uvula is generally not considered a serious condition, it can cause discomfort, difficulty swallowing, and obstruct the airway in severe cases. Seeking medical attention is advisable for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Home remedies and over-the-counter options can provide relief for mild cases of uvulitis, while more severe cases may require targeted medical interventions. By addressing the underlying cause and managing symptoms, individuals can effectively alleviate the discomfort associated with uvulitis and promote a swift recovery.