Cardiovascular
What Is CKM Syndrome? American Heart Association Identifies New Condition That Links Heart Disease, Kidney Disease, Obesity
What Is CKM Syndrome?
CKM syndrome is a systemic disorder characterized by reduced function in the kidneys, metabolism, and heart. By defining the syndrome, the AHA aims to highlight the interconnected nature of obesity, insulin resistance, chronic kidney disease, and cardiovascular disease; increase prevention; and encourage health care providers across different specialties to work together and embrace more holistic patient care approaches.
Two primary components of CKM are metabolic syndrome and chronic kidney disease. Characterized by abdominal obesity, high blood sugar, and hypertension, metabolic syndrome can lead to heart and blood vessel problems, making the development of cardiovascular disease subtypes such as coronary heart disease, cerebrovascular disease, peripheral artery disease, cardiac arrhythmias, and heart failure more likely. It can even lead to Type 2 diabetes, increasing the risk of developing kidney and vascular diseases.
Chronic kidney disease also raises the likelihood of heart and blood vessel problems. In fact, cardiovascular disease is the most common cause of death among chronic kidney disease patients. According to AHA’s advisory, just 10% of those with chronic kidney disease survive long enough to reach kidney failure. The authors noted that chronic kidney disease is a proinflammatory condition that, in addition to contributing to heart and blood vessel problems, can lead to complications like anemia and bone mineral metabolism issues that exacerbate cardiovascular disease. Meanwhile, heart problems, particularly heart failure, can contribute to chronic kidney disease. And issues with blood vessels, such as atherosclerosis, can affect kidney blood vessels, leading to resistant hypertension and kidney failure.
The Stages of CKM Syndrome
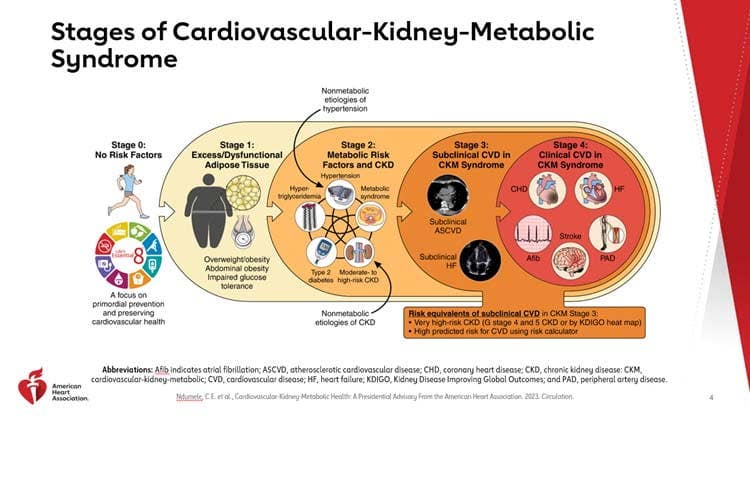
Recognizing that early detection represents an opportunity for intervention, the authors outlined the following five stages of CKM syndrome.
- Stage 0: In Stage 0 of CKM, a person is not overweight or obese and does not have chronic kidney disease, cardiovascular disease, metabolic risk factors, or impaired glucose tolerance. This stage is most common among young children, adolescents, and young adults. AHA recommends that school programs encourage healthy eating and physical activity to help reduce weight gain and improve heart health. For young adults, avoiding weight gain can reduce the likelihood of developing CKM syndrome risk factors, including metabolic syndrome and prediabetes or diabetes.
- Stage 1: Individuals are overweight or suffer from obesity, abdominal obesity, and/or dysfunctional adipose tissue without the presence of other metabolic risk factors or chronic kidney disease. They may also have impaired glucose tolerance or prediabetes.
- Stage 2: Conditions include hypertension, Type 2 diabetes, metabolic syndrome, and/or chronic kidney disease.
- Stage 3: This stage focuses on individuals who show signs of subclinical atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (encompassing such conditions as coronary artery disease, peripheral artery disease, carotid artery disease, and aortic disease) or heart failure along with CKM syndrome risk factors or chronic kidney disease.
- Stage 4: This stage includes patients with clinical cardiovascular disease with excess body fat and other metabolic risk factors and/or chronic kidney disease. It is divided into two subgroups: 4a for those without kidney failure and 4b for those with kidney failure. Individuals may have previously suffered a stroke, heart attack, or heart failure.
“The main takeaway from my perspective is the fact that there really is no prevention; there’s only intervention,” says Columbus Batiste, MD, FACC, FSCAI, co-founder of Healthy Heart Nation. “Everyone is at risk for disease. The way [the AHA] characterized it was not ‘healthy and normal,’ and then stage one. [Instead] they say, ‘CKM Stage 0.’ I think that sets the tone.”
Still, Batiste says, “I would love for them to go a little bit more in-depth with a lot of the strong data we know about the benefits of a whole-food, plant-based diet.”
For example, a 2021 meta-analysis of nearly 100 studies found that diets focused on plant-based foods that limit consumption of refined cereals and starches are associated with a lower cardiovascular risk than diets that include mostly animal foods. Additionally, increasing your alkali intake by eating a diet rich in fruits and vegetables may help reduce urinary markers of kidney damage in stage 2 chronic kidney disease patients.
But diet is just one part of the equation: Batiste also emphasizes the critical role exercise plays in helping individuals reduce excess belly fat. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommend adults aim for at least 150 minutes of exercise per week, or 30 minutes a day for five days a week.
“I always like to tell patients that it’s about lifestyle exercise,” Batiste says. “That means gardening, that means sweeping, it means vacuuming, it means climbing stairs. … Simple things actually add up to an awful lot, so a person doesn’t have to engage in hour-long brutal workouts to still glean the benefit of just basic, simple walking.”
To learn more about a whole-food, plant-based diet, visit our Plant-Based Primer. For meal-planning support, check out Forks Meal Planner, FOK’s easy weekly meal-planning tool to keep you on a healthy plant-based path.