Blood
Smart Ring Measures Blood Pressure
Continuous blood pressure monitoring has always been a major challenge for the biohacking community. Those giant arm cuffs aren’t exactly the kind of thing you want to wear all day and the wrist monitors aren’t super great either. So, [Kaan] and his research team set out to create a better continuous blood pressure monitor. This time as a ring.
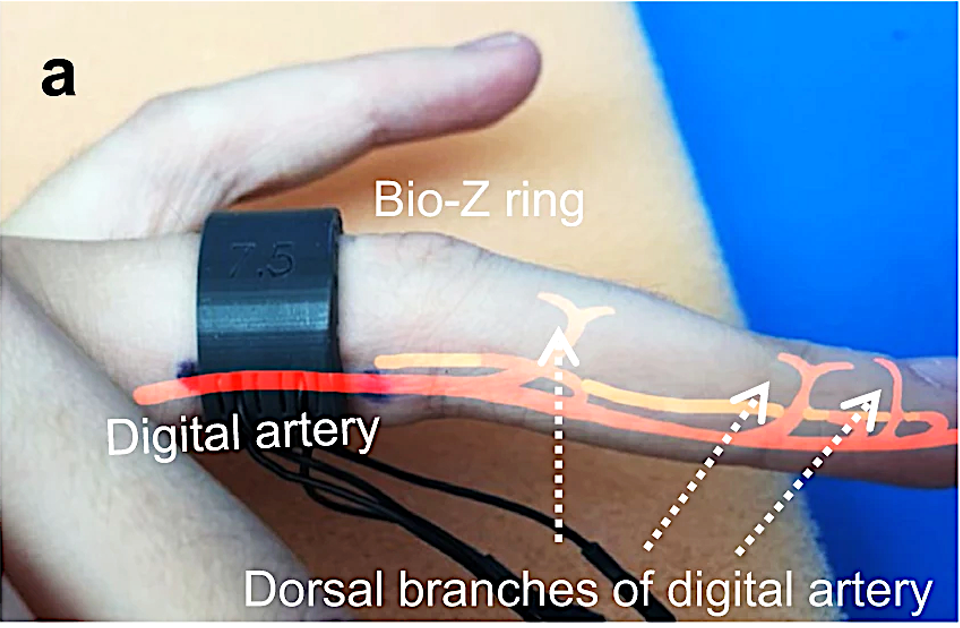
When your heart beats, the volume of blood in the blood vessels increases ever so slightly. This increase in volume results in a decrease in electrical impedance because blood is fairly conductive. We’ve seen a similar volume measurement using light for detecting heart rate, but [Kaan] says with impedance, you won’t need to worry about the effect of skin tone on the accuracy of the measurement.
As far as the hardware is concerned, they inject a small, constant 10 kHz sinusoidal current into the finger through 2 current-injecting electrodes, and then measure the resulting voltage drop across the finger with two sensing electrodes, a standard 4-probe Kelvin approach. Their results seem pretty good. They are within 5.27 millimeters of mercury (mmHg) of the gold standard for systolic blood pressure and 3.87 mmHg for diastolic blood pressure across 10 subjects, which they say are within the American Association for the Advancement of Medical Instrumentation’s (AAMI) guidelines. That’s definitely something to catch your attention.
We’ve seen several attempts to measure blood pressure using the analogous photoplethysmography technique, but those generally don’t seem to work out. Will the impedance plethysmography approach overcome the optical technique’s shortcomings? Only time will tell.