Infection
Airborne virus infectivity can be reduced by up to 99.98% by commercially available NPBI-based air purifiers, per experiment using real-world concentrations of COVID-19 strains, flu and RSV viruses
image:
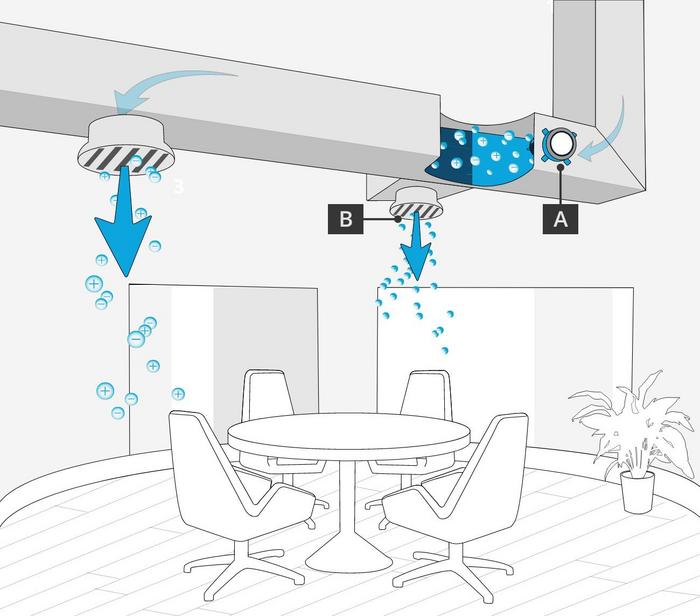
The drawing illustrates the delivery of positive and negative ions into a room. Ions generated by the in-duct NPBI device (A) are delivered into the room through diffusers (B) on the supply side of the HVAC system.
view more
Credit: GPS Air, CC-BY 4.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/)
Airborne virus infectivity can be reduced by up to 99.98% by commercially available NPBI-based air purifiers, per experiment using real-world concentrations of COVID-19 strains, flu and RSV viruses
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0293504
Article Title: Bipolar ionization rapidly inactivates real-world, airborne concentrations of infective respiratory viruses
Author Countries: USA
Funding: The authors received no specific funding for this work. All research and 3rd party laboratory testing was funded entirely by GPS Air. Edward Sobek is an employee of GPS Air and Dwayne Elias is a paid expert consultant for GPS Air.
Journal
PLoS ONE
Article Title
Bipolar ionization rapidly inactivates real-world, airborne concentrations of infective respiratory viruses
Article Publication Date
22-Nov-2023
COI Statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Disclaimer: AAAS and EurekAlert! are not responsible for the accuracy of news releases posted to EurekAlert! by contributing institutions or for the use of any information through the EurekAlert system.