Health Care
How to Remove a Comedo
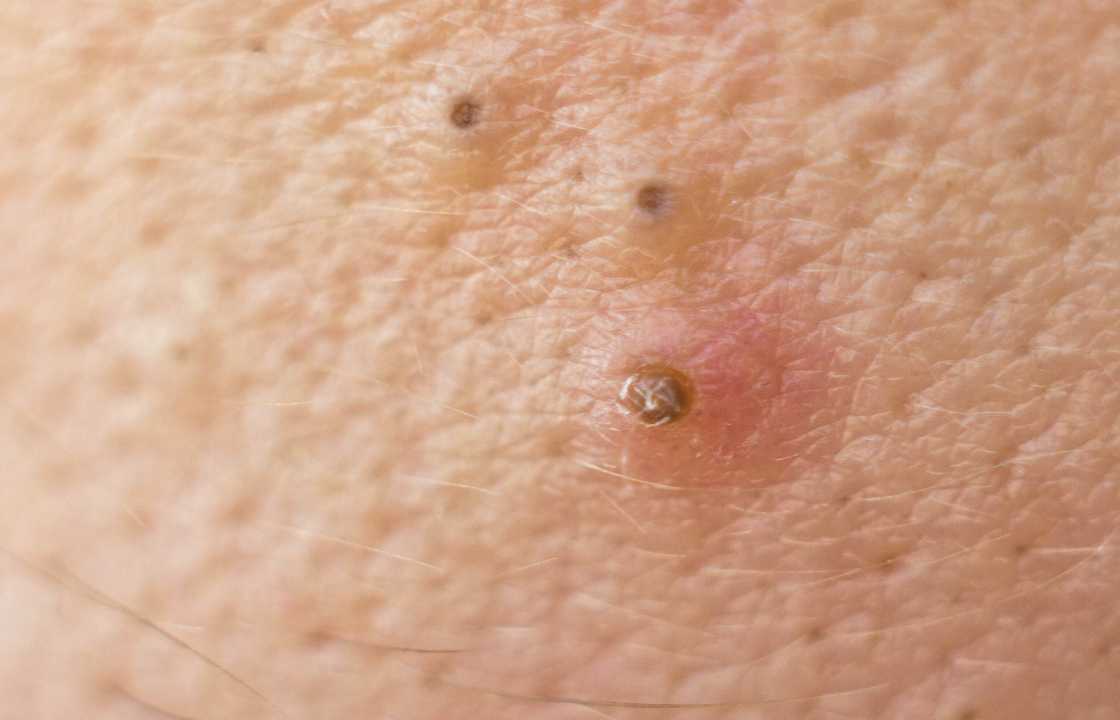
Comedones, a term that has become increasingly familiar, particularly to those who have perused the engaging world of pimple-popping videos online, represent the ubiquitous and pervasive facet of acne – a shared dermatological experience among many. In the realm of dermatology, this classification serves as a versatile descriptor for a wide spectrum of acne blemishes, each bearing its own distinctive characteristics and appearances. These blemishes may manifest as either the conspicuously white-topped whiteheads or the more visually striking black-topped blackheads, all of which collectively fall under the broad umbrella of comedonal acne. The reality is that nearly everyone, at some point in their lives, encounters the presence of these comedones, making them a universal aspect of the human experience. While these acne formations tend to be less inflamed and painful in comparison to other, more severe forms of acne, they still carry a significant impact, not merely in terms of physical discomfort but also with regard to their potential to dent one’s self-esteem. These pesky blemishes can often be perceived as unsightly, prompting individuals to seek solutions that not only alleviate their physical presence but also restore a sense of confidence and self-assuredness.
Comedones, which are frequently colloquially referred to as pores or hair follicles, undergo a complex and multifaceted process of obstruction due to an interplay of various factors, most notably the amalgamation of bacteria, excess sebum (oil), and the accumulation of dead skin cells. This intricate combination culminates in the development of these unassuming yet conspicuous small bumps on the skin’s surface. Despite being relatively less painful compared to other forms of acne, the notoriety of comedones primarily revolves around their often unsightly appearance, provoking individuals to seek solutions for their removal. This phenomenon is influenced by a multitude of variables, including genetic predisposition, hormonal fluctuations, and lifestyle factors, all of which can increase the likelihood of developing comedonal acne. Furthermore, environmental and behavioral factors also play a role in their emergence, with the usage of heavy styling products and the tendency to sport tight-fitting hats acting as potential contributors to the formation of comedones, frequently observed in the regions surrounding the hairline and forehead. Understanding the intricate dynamics behind comedonal acne is crucial for devising effective strategies to prevent and manage these unwanted skin imperfections.
In this comprehensive exploration of comedones, we will delve into their types, treatment options, and methods for preventing and managing these bothersome blemishes.
Types of Comedo
Comedones can be categorized into two primary types: whiteheads and blackheads, each distinguished by its appearance on the skin’s surface.
- Whiteheads: Whiteheads are essentially blocked pores that have closed over. They typically match the color of your skin or may be slightly lighter than the surrounding skin. Unlike some forms of acne, whiteheads are generally not painful. Individuals may experience whiteheads as solitary blemishes or in clusters.
- Blackheads: Blackheads, on the other hand, are identifiable by a dark spot on top. These blemishes differ from whiteheads in that the pore remains open, allowing the trapped oils and dead skin cells to be exposed to the air. This exposure to oxygen results in the characteristic dark coloring of blackheads.
Treating Comedones
Comedones are among the most straightforward types of acne to manage, given their proximity to the skin’s surface. Over-the-counter topical treatments, commonly containing ingredients such as benzoyl peroxide or salicylic acid, are effective in treating these blemishes. These products can be conveniently accessed and applied at home to alleviate comedonal acne.
However, for individuals with more stubborn or severe cases, consultation with a healthcare professional is advisable. Dermatologists can prescribe prescription-strength creams or oral medications tailored to address comedones. In some instances, antibiotics may also be recommended if bacterial infection is exacerbating the condition.
Extracting Comedones
While videos of doctors extracting comedones have gained popularity online, it is essential to exercise caution when attempting to replicate these procedures at home. Unsupervised extractions can lead to skin damage, infections, and scarring, thereby worsening the situation. It is advisable to seek professional guidance and treatment to safely and effectively manage comedones.
Other Types of Acne
Comedones are just one type of acne, and individuals may experience various forms of blemishes on their skin. Some other types of acne, often characterized by redness and inflammation, tend to be deeper and more resistant to over-the-counter treatments. These forms of acne include:
1. Papules: Raised, headless bumps that may feel rough or sandpapery to the touch.
2. Pustules: Raised blemishes filled with white or yellowish fluid, often requiring prescription medication for treatment.
3. Nodules: Deep, red, and larger-than-average blemishes that heal slowly and are hard to the touch.
4. Cysts: Inflamed, fluid-filled spots that can lead to scarring if left untreated and typically require medical intervention.
Preventing Comedo Breakouts
Taking preventive measures can significantly reduce the occurrence of comedonal breakouts. Here are some practical steps to consider:
1. Regular Face Cleansing: Wash your face with a gentle cleanser twice a day and after sweating.
2. Gentle Skin Care: Avoid abrasive or drying products and opt for lukewarm water instead of hot water. Refrain from scrubbing your skin roughly, and use your fingers for washing instead of abrasive tools.
3. Hair Hygiene: Regularly shampoo to keep your hair and scalp clean, preventing breakouts near your hairline and scalp.
4. Hands Off: Avoid picking or popping blemishes, as this can worsen the condition and lead to scarring. Touching your face can also spread bacteria, potentially causing infections.
5. Dietary Considerations: Be mindful of your diet and consider reducing dairy and simple carbs like refined wheat products.
By adopting these practices and maintaining proper skincare, you can effectively prevent and manage comedones, as well as other forms of acne. If you have questions or concerns about acne or the removal of comedones, it is advisable to consult with a medical professional for personalized guidance and treatment options.
In conclusion, understanding comedones and their management is essential for those looking to maintain clear and healthy skin. Through proper skincare, informed choices, and consultation with healthcare professionals, individuals can effectively navigate the challenges posed by comedonal acne and other types of blemishes.