Insight, Reproductive, Syndrome
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: What you need to know
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a widespread hormonal disorder that afflicts millions of women across the globe. It is a complex condition that can manifest through an array of symptoms, including irregular menstrual cycles, excessive hair growth, acne, and weight gain. Despite its prevalence, PCOS often remains underdiagnosed and misunderstood, making it crucial to elucidate what PCOS is, its underlying causes, the varied symptoms it presents, potential complications, methods for diagnosis, available treatment options, and strategies for effectively living with this condition.
Understanding Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
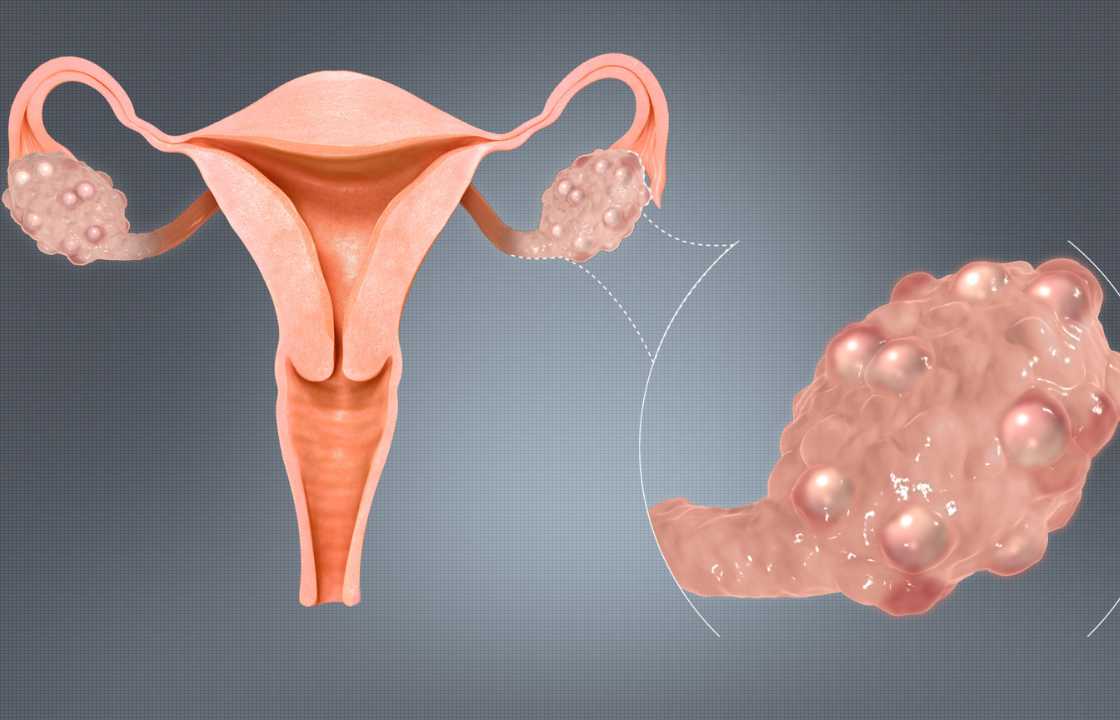
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome, or PCOS, is a hormonal disorder impacting the ovaries, which serve as the reproductive organs responsible for producing eggs and essential hormones. In women with PCOS, there is an overproduction of androgens, male hormones like testosterone, leading to a range of distressing symptoms. These elevated androgen levels can result in irregular menstrual periods, weight gain, acne, and the development of excess facial, chest, or back hair. The term “polycystic ovary” pertains to the appearance of the ovaries when observed through ultrasound, often displaying multiple small cysts on their surface.
The Complex Causes of PCOS
While the precise origins of PCOS remain elusive, it is widely believed that a combination of genetic and environmental factors is at play. Insulin resistance, in particular, is thought to be a significant contributor. Insulin resistance can lead to heightened insulin levels in the bloodstream, prompting the ovaries to produce excess androgens, consequently leading to the characteristic symptoms of PCOS. Other factors that might elevate the risk of developing PCOS include obesity, a sedentary lifestyle, and certain medical conditions, such as thyroid disorders.
Symptoms of PCOS: A Varied Spectrum
The presentation of PCOS symptoms can vary from one individual to another. However, the most common indicators encompass irregular menstrual cycles, hirsutism (excessive hair growth) on the face, chest, and back, acne, weight gain, and difficulties in conceiving. PCOS may also contribute to mood swings, depression, and anxiety. Beyond the physical symptoms, PCOS can exert emotional and psychological effects, affecting self-esteem and body image. It is vital to engage in regular consultations with a trusted gynecological specialist, emphasizing the importance of professional guidance and care in managing PCOS.
Potential Complications Arising from PCOS
PCOS elevates the risk of several health-related complications, including the development of type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, and elevated cholesterol levels. Sleep apnea, a condition characterized by interruptions in breathing during sleep, is more prevalent among women with PCOS. Furthermore, PCOS increases the susceptibility to endometrial cancer, a malignancy that targets the lining of the uterus. The management of PCOS is, therefore, not solely about alleviating symptoms but also mitigating these potentially severe complications.
The Diagnostic Challenge of PCOS
Diagnosing PCOS can be challenging, as there is no singular test that can definitively confirm the condition. Healthcare providers typically rely on a combination of factors, including patient-reported symptoms, physical examination, and blood tests, to make a diagnosis. In certain cases, an ultrasound may be employed to assess the ovaries for cystic formations. It is essential to acknowledge that the diagnostic criteria for PCOS have evolved over time, and there is ongoing debate among healthcare professionals regarding the most effective diagnostic approaches.
Navigating the PCOS Treatment Landscape
While there is no definitive and complete cure for Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS), it is important to understand that a range of treatment options exists, each specifically tailored to address the multifaceted nature of the condition and its associated symptoms. Managing PCOS often involves a comprehensive approach that combines medical, dietary, and lifestyle strategies.
Lifestyle modifications, for instance, emerge as a foundational pillar in PCOS management. Regular physical activity and a well-balanced diet are instrumental in regulating insulin levels and mitigating the potential for weight gain, which can be a common concern for individuals with PCOS. These healthy habits serve not only to alleviate symptoms but also to foster long-term well-being.
Additionally, healthcare professionals may prescribe medications as part of the treatment plan. Birth control pills, for example, can help regulate menstrual cycles and hormonal imbalances. Metformin, a medication primarily used to manage diabetes, can also be recommended to lower insulin levels, which are often elevated in individuals with PCOS.
In more severe cases or when cysts become problematic, surgical interventions may be deemed necessary to remove ovarian cysts and alleviate associated pain or complications. These surgical procedures are typically performed by skilled surgeons with expertise in gynecological issues.
For women with PCOS who aspire to conceive, the journey may require specialized fertility treatments. Ovulation induction, a method to stimulate egg release, and in vitro fertilization, a process that combines eggs and sperm in a laboratory setting, offer hope and can significantly improve the chances of successful pregnancy.
In conclusion, while a complete cure for PCOS remains elusive, it is comforting to know that a multifaceted approach to treatment is available, empowering individuals with PCOS to manage their symptoms, improve their overall health, and pursue their desired life goals, including the dream of parenthood. Consulting with healthcare professionals is the first step on the path to managing PCOS effectively and enhancing one’s quality of life.
Strategies for Empowered Living with PCOS
Living with PCOS can be a challenge, but with the right treatment and support, it is possible to effectively manage the condition and lead a healthy, fulfilling life. Women grappling with PCOS should prioritize self-education about the condition, foster a deep understanding of their specific symptoms, and establish a close partnership with their healthcare providers to formulate a personalized treatment plan. Regular check-ups and screenings are instrumental in identifying potential complications and monitoring the efficacy of treatment regimens. Beyond medical intervention, several lifestyle modifications can be embraced by women with PCOS. These include maintaining a healthy weight through exercise and adopting a balanced diet to regulate insulin levels and decrease the risk of associated health issues. Incorporating stress-reduction practices such as yoga, meditation, and mindfulness can further enhance one’s ability to manage PCOS effectively.
In summary, Polycystic Ovary Syndrome is a prevalent hormonal disorder affecting women globally. While it lacks a cure, there exists an array of treatment options for symptom management and complication prevention. Coupled with these medical interventions, embracing a health-conscious lifestyle and stress management techniques can significantly enhance the quality of life for individuals with PCOS. By fostering awareness and seeking professional guidance, women with PCOS can embark on a journey towards a healthy and fulfilling life.