Health Care, Insight
What Is Chelation Therapy?
The human body is a complex system that can be vulnerable to various toxins, including metals such as lead, mercury, iron, and arsenic. When these metals accumulate within the body, they can become toxic, potentially leading to a range of health problems. Chelation therapy, a medical treatment, is designed to address this concern by employing specific medications to eliminate these toxic metals from the body, preventing them from causing harm.
Chelation therapy is primarily recognized for its efficacy in treating metal poisoning, but it has also been suggested as a potential treatment for conditions like heart disease, autism, and Alzheimer’s disease. However, the effectiveness of chelation therapy in treating these conditions remains a topic of debate, and its use in these contexts is not universally supported within the medical community. Furthermore, it’s important to note that chelation therapy carries potential risks, including serious side effects and even death if not administered correctly.
How Does Chelation Therapy Work?
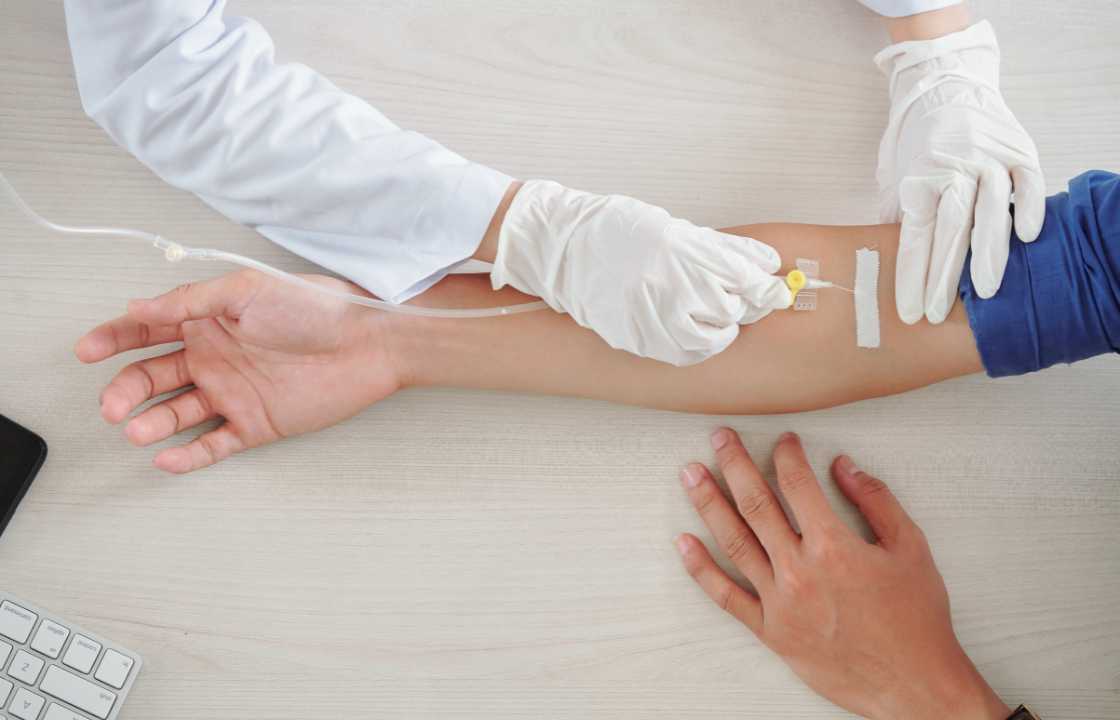
Chelation therapy relies on specific medications that have the ability to bind to metals present in the bloodstream. These medications are typically administered via an intravenous (IV) tube inserted into the patient’s arm, but they are also available in pill form. Once the chelating medication binds to the metal, both the medication and the toxic metal are excreted from the body through urine.
The metals that can be effectively removed through chelation therapy include lead, mercury, and arsenic. Before undergoing this treatment, a blood test is typically conducted to confirm the presence of metal poisoning.
Conditions Treated with Chelation Therapy
While chelation therapy is medically approved to treat metal poisoning, there is significant debate and limited scientific evidence regarding its effectiveness for other conditions. Some alternative health care providers and supplement companies claim that chelation therapy can alleviate symptoms associated with autism, Alzheimer’s disease, and heart disease. However, these claims are not universally accepted within the medical community.
Here’s an overview of what current research suggests about chelation therapy for these three conditions:
1. Autism: Some proponents of chelation therapy for autism believe that it can improve symptoms by removing metals, particularly mercury, from the body. However, scientific studies have refuted the idea that mercury in childhood vaccines causes autism. The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) asserts that there is no evidence supporting the effectiveness of chelation therapy for autism, and it may pose risks. In fact, a tragic case where a child died after undergoing this treatment highlights the potential dangers. The AAP recommends chelation therapy for autism only within the framework of a clinical trial.
2. Alzheimer’s Disease: Alzheimer’s disease is characterized by the accumulation of abnormal proteins, tau and beta-amyloid, in the brain, leading to damage. While some researchers have proposed that the buildup of metals like copper, iron, and zinc may play a role in the development of Alzheimer’s, there is currently no concrete evidence that chelation therapy effectively treats this condition.
3. Heart Disease: Heart disease often results from the formation of fatty deposits, known as plaques, in the arteries. These plaques can narrow blood vessels and reduce flexibility, limiting blood flow. Chelation therapy aims to remove these plaques by binding to calcium found in artery plaques. In 2002, the National Institutes of Health conducted a study called TACT, which indicated a slight reduction in the risk of heart attacks, strokes, and other heart problems with chelation therapy, but this effect was primarily observed in individuals with diabetes. The study, however, did not provide conclusive evidence for the treatment of heart disease using chelation therapy. Consequently, the FDA has not approved this therapy for heart disease, and further research, such as the ongoing TACT2 study, is needed to establish its efficacy.
Side Effects and Considerations
Chelation therapy can indeed be safe and effective when administered by experienced healthcare professionals and applied to the precise medical conditions for which it has been approved. It is crucial to recognize that common side effects associated with chelation therapy encompass a range of symptoms, including a mild burning sensation at the intravenous (IV) site, as well as occasional occurrences of fever, headache, and episodes of nausea or vomiting. These side effects, while generally manageable, underscore the importance of medical supervision during the treatment.
However, it is essential to delve into a deeper understanding of the potential risks associated with chelation therapy. Chelating drugs, in their process of binding to and eliminating harmful metals, can inadvertently sequester essential metals that the body relies on for proper functioning. These vital elements, such as calcium, copper, and zinc, play pivotal roles in various biological processes. The inadvertent removal of these essential metals may result in the development of deficiencies that can have a cascade of adverse effects on the body’s health.
In particular, individuals who have undergone chelation therapy have reported cases of low calcium levels in their blood, a condition known as hypocalcemia. Low calcium levels can lead to a multitude of health issues, affecting nerve and muscle function, blood clotting, and bone strength. Additionally, there have been instances of kidney damage associated with chelation therapy, further emphasizing the need for careful monitoring and expert medical oversight during treatment.
This underscores the importance of conducting a thorough risk-benefit analysis when considering chelation therapy and the critical role that healthcare professionals must play in evaluating its appropriateness for an individual’s specific medical condition, thereby minimizing potential complications and ensuring the patient’s overall well-being.
The Importance of Evidence-Based Medicine
Furthermore, it is vital to underscore that chelation therapy, while FDA-approved for metal poisoning, remains a topic of ongoing research and debate in the medical community. While it can be a life-saving treatment for acute metal poisoning incidents, its application in chronic conditions such as Alzheimer’s or heart disease lacks a solid foundation in clinical trials and long-term studies. In such cases, opting for unproven chelation therapy may pose serious health risks, including potential adverse effects.
Given the potential dangers associated with chelation therapy when misused or unsupervised, individuals should exercise a high degree of caution when considering alternative treatments for non-metal poisoning conditions. Evaluating the credibility of online products or healthcare providers promoting chelation therapy is essential to protect your well-being. Be especially vigilant when addressing health concerns related to chronic diseases, and always prioritize seeking medical advice from qualified professionals who can provide evidence-based guidance.
Furthermore, it is important to reiterate that chelation products, even for FDA-approved uses, should never be utilized at home without the supervision and prescription of a licensed medical practitioner. The intricate nature of chelation therapy demands precise dosing and careful monitoring to avoid potential complications. Therefore, scheduling a consultation with your healthcare provider to discuss the suitability of chelation therapy for your specific medical condition and to ensure its safe and effective administration is an absolute imperative. Your doctor can provide personalized guidance based on your unique health circumstances, ensuring your well-being and safety throughout the treatment process.